Innovative technologies in health care improve the quality of services provided and patient safety. Electronic health records (EHR), computerized physician order entry (CPOE), and other systems work together to provide quick and effective care. One such system is the barcode medication administration (BCMA), which uses technology to prescribe and administer drugs by scanning the barcode to obtain patient and medication information (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017). Despite the significant benefits BCMA has brought to medical practice, its implementation still faces challenges that must be addressed.
Medication is critical in treating patients, and mistakes in their administration can lead to severe consequences. To ensure the drug is correct, it is essential to know the rule about five rights: the right patient, the right time and frequency, the right drug, the right dose, and the right route (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017). BCMA helps to ensure all rights and, as studies demonstrate, significantly reduces the likelihood of medication errors (Thompson et al., 2018). As a result, bar codes optimize nurses’ work and enhance patient safety.
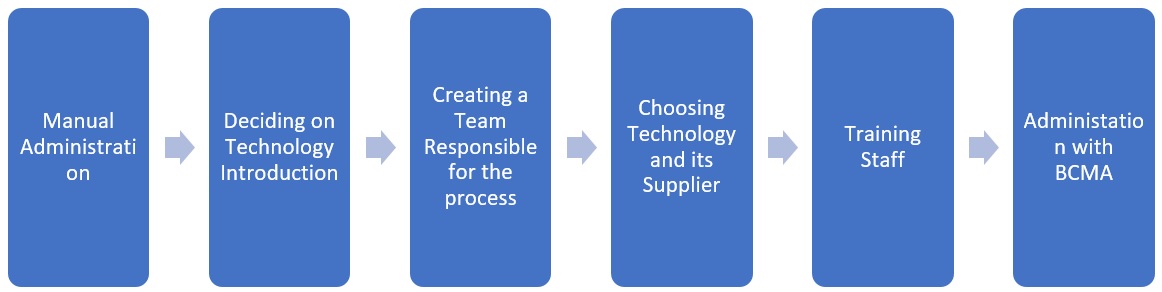
Introducing technology into hospital workflows is a long and complex process. Traditionally, manually prescribing and administering medicine, doctors write the necessary medicine in the medication record, which is sent to the pharmacist (Naidu & Alicia, 2019). After preparation, the drug is directed to the ward, where the nurse picks it from the cart and gives it to the patient (Naidu & Alicia, 2019). This approach increases the likelihood of errors due to the human factor, such as incomprehensible handwriting. With BCMA, hospitals need the Internet, barcodes, scanner, and appropriate software. To implement it, they must assemble a team responsible for the process, select the technology and its supplier, and train the staff to use the system (McBee et al., 2019). The change from manual administration to the use of bar codes is shown in the flowchart (see fig. 1).
The implementation and use of BCMA still have some problems and challenges. For instance, pharmacists labeling drugs can make errors, and codes may be printed or misread (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2017). Moreover, technology adoption is often accompanied by resistance to change, as processes and systems can seem very complex to employees (Naidu & Alicia, 2019). The system can malfunction without the necessary technical support and knowledge, and cyber security violations will occur (Naidu & Alicia, 2019). To overcome these issues, institutions should choose a reliable supplier and carefully educate personnel while demonstrating the system’s advantages. Trained employees will be better able to cope with changes and manage new processes efficiently.
Thus, technology is changing health care and work processes in hospitals. The BCMA suggests using barcodes to administer drugs more precisely and avoid errors. The system has proven its effectiveness and can bring significant advantages to the hospital. Implementing the new technology requires several steps, in particular, the assignment of the responsible team, the selection of technologies, and the personnel training. The BCMA may still have problems, but employees’ education and careful choice of technology will help deal with them.
References
McBee, D. N. P., Marie, E., Kuhlmann, D. N. P., & Patterson, D. N. P. (2019). What you need to know about bar-code medication administration. Journal of Nursing & Interprofessional Leadership in Quality & Safety, 2(2), 1-8.
McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. (2017). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge (4th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Naidu, M., & Alicia, Y. L. Y. (2019). Impact of bar-code medication administration and electronic medication administration record system in clinical practice for an effective medication administration process. Health, 11(5), 511-526.
Thompson, K. M., Swanson, K. M., Cox, D. L., Kirchner, R. B., Russell, J. J., Wermers, R. A., Storlie, C. B., Johnson, M. G., & Naessens, J. M. (2018). Implementation of bar-code medication administration to reduce patient harm. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Innovations, Quality & Outcomes, 2(4), 342–351.