Executive Summary
The use of health data analytics enables better patient care, personalized treatment, better decision making, and faster diagnosis that are more accurate. Incorporating data analytics in the business model helps the business optimize performance and reduce costs, among other benefits. With the current trend of rapid digitization, healthcare providers are compelled to adopt electronic systems for collecting and storing data. Meanwhile, digital data can be analyzed to reduce costs and health risks and assist in research and technology. Practical application of data analytics in healthcare can potentially streamline and improve the outcome of healthcare. Data analytics in healthcare offer both estimation and exploration capability for information.
Industry Problem
Provision of effective health through prevention, diagnosis, amelioration, and treatment is challenged by errors, alleviated risks, unequal distribution of health facilities, and high prices. However, the increasing volume of data collected in health facilities, including patient information, clinical data, financial data, operational data, and medical knowledge, can be leveraged to tackle the challenges. Healthcare information technology (H.I.T.) is evolving into digital health informatics and taking the initial step in filling the gaps inefficient healthcare systems (Meeto et al., 2018). Health Informatics creates business intelligence in the healthcare industry to reduce healthcare costs, facilitate speculation in health care and improve patient care. The tools and systems used to collect, store, share and analyze health data are electronic health records (E.H.R.s), personal health records (PHRs), master patient indexes, and health-related patient portals. Data analytics in health care is aiding healthcare providers to keep track of diagnosis, patient response, and demographic distribution of diseases to streamline healthcare operations.
E.H.R.s, PHRs, administrative data, claims data, clinical trial databases, and patient portals are the data resources used to manage costs, health risks, research, and innovation. At the point of care, electronic and personal health records including cure, drug prescriptions, laboratory tests, and physiologic testing data, are obtained (Veinot et al., 2019). Data collected by hospitals about their operations will enable the organizations to assess how accurately they are achieving intended goals. Clinical trial databases establish the relationship between different groups in medical research. Patient registries such as portals provide a narrow range of critical data, especially for managing chronic conditions such as cancer.
Data Sources
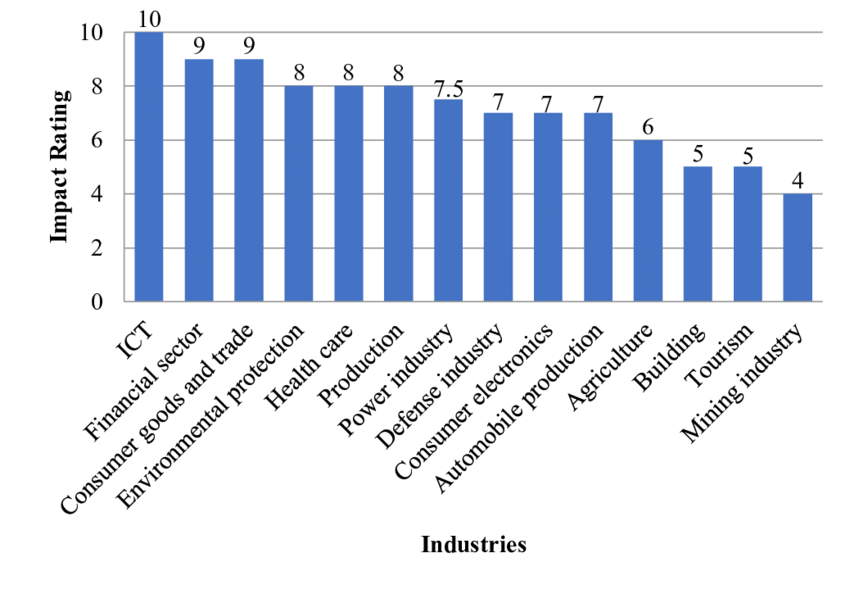
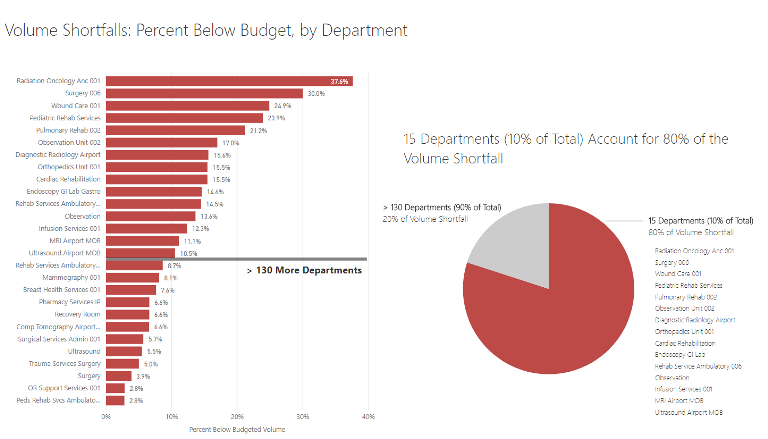
Analysts in the healthcare industry can source data from internal records from external sources such as historical clinical trial data to improve the estimation of relevant parameters. Healthcare is among the most affected industries by data analytics illustrated in figure 1 below (Ilin et al., 2019). E.H.R.s, PHRs, and administrative data can be sourced internally, whereas claims data and clinical trial databases can be found in external sources. The E.H.R.s and PHRs, are recorded in the hospitals collected from various patients in inpatient and outpatient care. Data analytics in hospitals determine the most essential services that need more investment and less utilized services that resources can be monitored to save on cost illustrated in figure 2 below. Administrative records such as drug catalogs, and admission, and discharge data are available in hospital services.
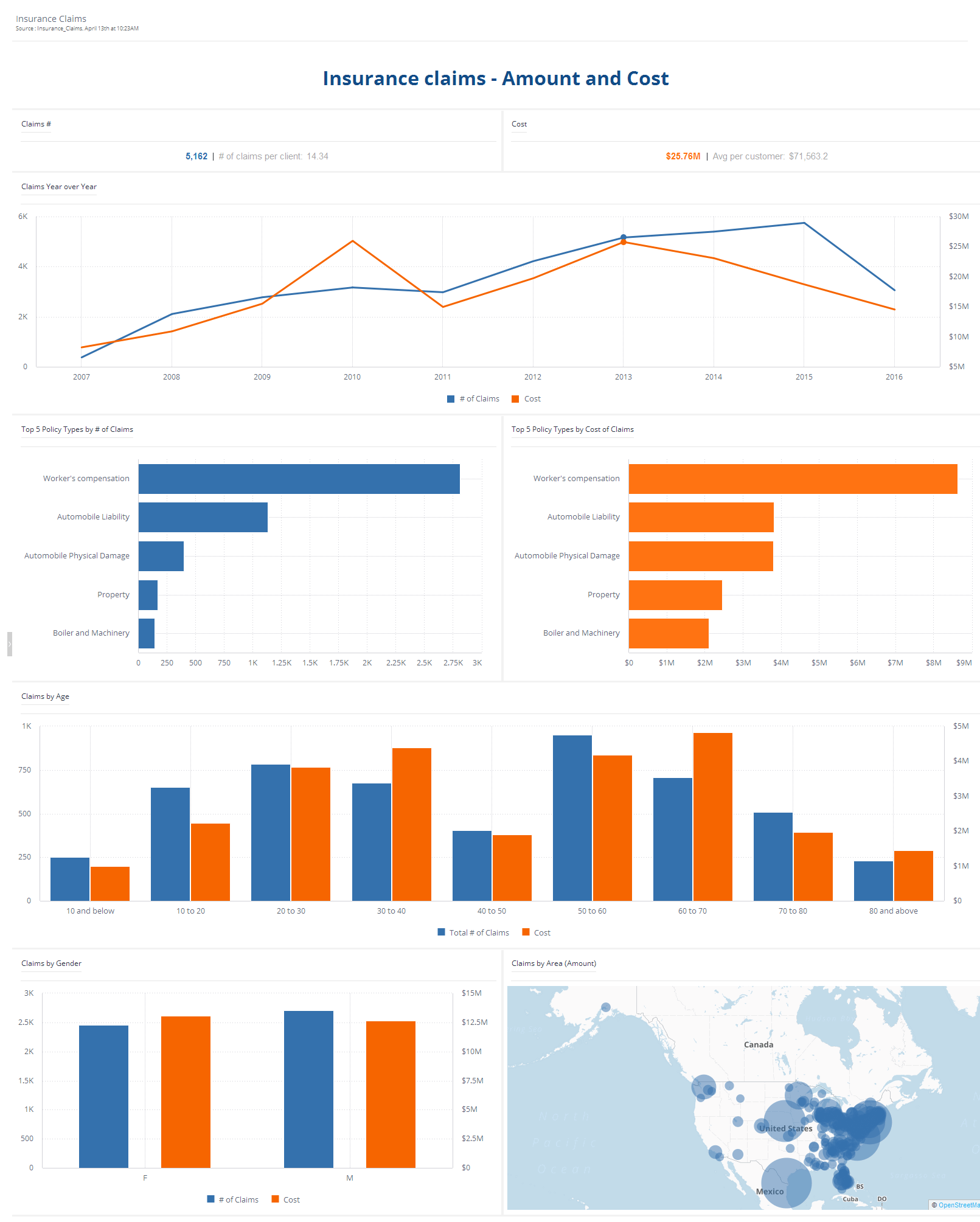
The Basic Stand Alone (B.S.A.) on medical care claims and the Medicaid statistical information system will summarize the payment for procedures in the insurance claims (C.M.S., 2021). B.S.A. contains data files on different healthcare claims such as prescription, inpatient, and outpatient claims for public use (Medicaid, 2021). Highlighted in figure 3 below data analytics claims significantly minimize losses of insurance claims. Medicaid statistical information presents a collection and utilization of claims data to improve the beneficiary of quality care. The U.S National Library of Medicine will provide the records of privately and publicly funded clinical studies around the globe.
Selecting the Business Problem
Large volumes of data associated with health care can be used to detect fraud, abuse, waste, and errors in healthcare charges and insurance claim costs hence reducing recurrent losses and facilitating enhanced patient care. The anomalies detected will enable public and private health providers to discover hidden costs that impact healthcare efficiency. The administrative data and claims data will be used in financial data analytics to cut costs and improve profitability in healthcare. Systematic analytical research will be used to explore the impacts of the sources on cost and recommend the best means of tracking and monitoring costs using health informatics and data analysis. Bearing the rapid evolution of health care in the digital age and large volumes of data in the medical care sector, the research problem is elemental to leverage the data and business analytics with the aim of cutting costs.
Patient information and records provide broader insights to the stakeholders in health care, enabling them to develop and manage strategic, tactical, and operational health systems in the most cost-effective manner. According to Wang et al. (2018), financial data in health care can also acknowledge leveraging cost-based incentives effectively. The cost directly impacts equal access to medical health (Brewer et al., 2020). Hospitals can use data analytic tools to identify patients with specific symptoms and diseases, determine the severity and incidence of various conditions and determine dispensable hence informed decision-making in financial resource allocation. By analyzing customer data, hospitals can identify the actual costs to serve that provide insights into strategic financial adjustments instead of cutting costs at random. Therefore, business analytics is a natural and strong fit in the healthcare industry to reduce costs and improve profitability, largely affecting the industry.
Clinical data create decision support systems that help predict patient stability, mortality, and symptoms. Poor documentation of healthcare records deteriorates the overall patient care, discourages diagnosis and treatment of new diseases, and affects the national health services (Gondi and Song, 2019). Accurate patient information and previous data records have some predictive value that assists clinicians with patient management and in allocating finite resources. H.I.T. can store, retrieve and analyze patient data, and improves patient safety by reducing medication errors, limiting adverse medication reactions, and improving compliance to practice guidelines (Sherman et al., 2019). Moreover, data analytics improves programming and staffing, provides patients with more appointment options, and lowers readmission rates by predicting high-risk patients based on demographic health data.
Consistent analysis of raw datasets indicates trends that facilitate demographic planning, effective policy decisions, allocation of resources, and prediction of outbreaks. Data analytics in healthcare affect strategic planning in resource allocation and accountability of health systems. Small amounts of data from individual patients can be linked up and pooled to highlight patterns that help in devising efficient healthcare systems (Mehta and Pandit, 2018). Planning involves setting predetermined goals based on the evaluation of relevant data. Standards on which actual performance is measured are provided by planning. Additionally, health records assist in research and innovation by providing critical information such as disease symptoms, risk factors, the outcome of various patients, and duration of care. Information about disease trends gives direction to research and innovation to develop prevention and treatment measures for the disease.
Reference List
Brewer, L.C., et al. (2020) ‘Back to the future: achieving health equity through health informatics and digital health.’ JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 8(1), p. e14512. Web.
C.M.S. (2021) ‘Basic Stand Alone (B.S.A.) Medicare claims Public Use Files (PUFS).’ CMS. Web.
Gondi, S. and Song, Z. (2019) ‘Potential implications of private equity investments in health care delivery.’ Jama, 321(11), pp.1047-1048. Web.
Ilin, I., Klimin, A. and Shaban, A. (2019) ‘Features of Big Data approach and new opportunities of BI-systems in marketing activities.’ E3S Web of Conferences 110, p. 02054.
Medicaid. (2021) ‘Transformed Medicaid Statistical Information System (T-MSIS).’ Medicaid, Web.
Meetoo, D., Rylance, R. and Abuhaimid, H.A. (2018) Health care in a technological world. British Journal of Nursing, 27(20), pp.1172-1177.
Mehta, N. and Pandit, A. (2018) ‘Concurrence of big data analytics and healthcare: A systematic review.’ International Journal of Medical Informatics, 114, pp.57-65. Web.
Sadineni, P.K. (2020) ‘Developing a model to enhance the quality of Health Informatics using Big Data.’ In 2020 Fourth International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud)(I-SMAC) (pp. 1267-1272). IEEE.
Sherman, J.D., MacNeill, A. and Thiel, C. (2019) ‘Reducing pollution from the health care industry.’ Jama, 322(11), pp.1043-1044.
Veinot, T.C., et al. (2019) ‘Leveling up: on the potential of upstream health informatics interventions to enhance health equity.’ Medical Care, 57, pp. S108-S114.
Wang, Y., Kung, L., Wang, W.Y.C. and Cegielski, C.G. (2018) ‘An integrated big data analytics-enabled transformation model: application to health care.’ Information & Management, 55(1), pp.64-79. Web.