Globalization is the process of integrating the different nations of the world by uniting their views, cultures, products, and ideas. Technology has aided a great deal in the promotion of globalization. Technology in transport and communication has enabled speedy, accurate, and less stressful access to information and places all over the world. One important aspect of contemporary world-economy is the role of the internet and mobile phones in helping to make the world a global village.
Globalization is very important and beneficial for the growth of the global economy. Globalization has both positive and negative impacts on the world economy whereby it affects the environment and the socio-economic setting of nations as discussed in this paper.
The main goal of globalization is to help further interaction and interdependence among nations regarding their economic, religious, political, educational, and social aspects. History traces the origin of efforts to globalize the world to the third millennium BCE, but other recent sources agree to the fact that it is not until the late 19th century and early 20th century that these efforts bore fruit1. Consequently, the globalization process began speeding faster than ever before2. In this period, several important innovations and discoveries took place that helped to connect further the world, such as the discovery of electricity, landlines, jet engines, cell phones, and the internet3.
Globalization is made up of the four most important aspects that include: the people’s movement and migration, trade and transaction, movement of capital and investment, and knowledge distribution. Since the 20th century, technology is the fast overtaking traditional use of gadgets, especially in communication. Gadgets that have gained a lot of popularity in today’s world include the computer, digital cellular phone, and the Internet. Computers are even more famous since they can be reprogrammed to fit into any use.
The Internet and mobile phone usage have risen drastically over the past two decades as per the data thereby providing the economic freedom that is the main building block of the international political economy4. For example, in the year 1990 mobile subscribers made up of twelve and a half million users, which was an equivalent of 0.25% of the total world population while internet users made up a total of two million and eight hundred thousand users, which was 0.05% of the world population.
In the year 2010, mobile phone subscribers consisted of four billion, which translates to sixty-eight percent of the total world population while internet users made up one billion and eight hundred thousand people and this translates to 26.6% of the total world population. This data shows that the world is increasingly being converted into a small sphere where a person from any corner of the world can have undeterred access to another far corner of the world in an instant. Furthermore, governments can use this provision to “play their role in economic freedom”5.
The term globalization has gained popularity in usage throughout the years with academicians, economists, and other world leaders using it for different purposes and contexts. The one person who has widely been credited with the popularization of the term was an economist called Theodore Levitt. Since then, the term has benefited from a host of definitions and used especially about the various issues about the international political economy.
For many years, the term globalization has been used to refer to the union of business activities. As mentioned earlier, with increase conception of technology in daily activities, businesses have been able to grow internationally. International business is a business that involves participants from two or more nations. After years of unsuccessful penetration into new markets, various multinational enterprises have their market shares located in more than just a few countries6. These companies include Samsung, Toyota, Coca-Cola, and Monsanto just to name a few. International trade is among the major sources of national revenue in some countries.
International trade may involve globalization of several production inputs such as labor where companies can outsource laborers from other countries’ raw materials and finished goods market. The need for globalization was particularly important after World War II when it became possible and necessary to make trade blocks, treaties, and havens. Due to the increased economic globalization, countries in the 21st century have come together to formulate laws, regulations, and specifications to guide international trade, ensuring the best benefit to their citizens and economies. Also, due to socio-cultural interaction, people around the world have been able to exchange ideas, intermarry, and disseminate ideas and values.
Currently, countries such as India, Singapore, Canada, and Britain have different social cultures but similar monetary policies7. The emergence of the new brand of cultures has led to the erosion of some cultures and the diminishing of some religious beliefs. In the next section, this paper will discuss the benefits and disadvantages of globalization in the context of the international political economy and about outside materials from various scholars.
Globalization has helped international firms to increase their productivity and therefore enhance their returns. In most cases, increased returns to a company go in line with increased revenue to the countries where the companies operate. The result of this scenario is that the world economy scales upwards. Hence, in this context, globalization is good. How productivity increases are probably the major question that economic analysts focus on.
Through globalization, nations have provisions and laws allowing citizens to work in other nations without being harassed. Therefore, it is common for nations to have special arrangements to provide visas to traders from specific areas around the world, and also the process of renewing these permits8. Therefore, a multinational company can be able to outsource employees from another country. When a company outsources employees, who have better skills, experience, and motivation than those from its resident nation, the productivity of that company is most likely to rise. On the other hand, the rise in productivity leads to global economic stimulus.
For example, in the USA there is a guest-workers program, which permits employers to sponsor people from other nations who are subject deportation if they do not acquire a green card before the end of the three years. In the year 2009, the United States of America had over one million workers who were on such a worker program.
Globalization also enables setting up of new businesses and fuels the growth of existing companies. Globalization may entail specific agreements between nations to share natural resources, which might be the raw materials required by the new companies to begin operation9. Besides, for some companies, the process and expense of acquiring raw materials from their parent countries may be logistically difficult and be marred by many hindrances.
However, through such agreements as mentioned above, these companies may access the raw material needed to operate and grow to higher levels. Business expansion promotes the growth of national and global economies. Moreover, globalization promotes immigration, which ultimately promotes the growth of the global economy. Due to globalization, it is easier for citizens of one country to migrate from one country to another, or from one continent to another. In a situation where one feels that there is a business opportunity in another country that he/she can take this chance and make it his/her economic activity.
In a globalized international economy, it is easy to migrate to that country and gather the necessary resources to undertake the business opportunity. These new businesses set up by immigrants provide employment opportunities raising the living standards of the local people. For example, every year high numbers of people from other continents move into the US to look for jobs, and some end up finding jobs. Talented individuals such as footballers from other nations move into developed countries in a bid to be hired and improve their skills, a chance they could not have had without free migration.
Globalization provides a larger market where companies can sell their products. As a result, the turnover rates of these companies increase thereby improving their performance and promoting growth. These kinds of situations lead to national, international, and global growth. Also, due to the availability of a large market, new companies can be established. The establishment of new companies provides employment and revenue to the government.
When a large number of people in a country are employed, they have a better purchasing power hence the general business activities in the country are promoted. Furthermore, due to the large proportion of the people being employed, there is less co-dependence as people can afford to live better. As a result, the governments can use the money it could have used to support such welfare courses for better ventures such as infrastructural development.
Globalization also enables firms to access the necessary factors of production such as finance10. Before the advent of globalization, firms could only access financial help from local firms, which were sometimes incapable or unwilling to risk a large pool of resources on certain business ventures. However, things have changed now, and companies can access finances from international firms such as international banks, investors, and insurance services from international providers.
Even though globalization promotes the economy of the world, it is also destructive and non-beneficial in many ways. Globalization may lead to a brain drain that may adversely affect some parts of the world. This phenomenon provides a fertile ground for the exchange of factors of production between nations including the outsourcing of staff. As a result, when a company or nation’s workforce does not feel well catered for in their home country it is outsourced to other nations, the former nation becomes deprived of its workforce. This situation may lead to a brain drain, which deprives a nation of an active workforce, thus lowering its productivity. Low productivity translates into a low performing national economy and most likely than not, this may also affect the global economy.
When a country spends a lot of resources educating and training its citizens and then they go and work in other nations, the skills gained are not utilized in the country. On the other hand, a country cannot set up successful economic activities unless it also hires from other countries. Sometimes there is reverse brain drain whereby a foreign company may establish a branch in a less developed country, yet instead of hiring skilled manpower from the nation, they come with their laborers from the developed countries11. This is what is referred to as reverse brain drain. Both the reverse and normal brain drain are non-beneficial to the host country. Reverse “brain drain can also occur when intellectuals from developed countries migrate to less developed countries to learn from their institutions or gain experience”12.
Globalization also leads to increased competition in small markets. Due to the opening up of a country’s market to the whole world, some markets become flooded with an increasingly high number of businesses such that the local business can no longer have the market share they enjoyed before. Lower market translates to fewer sales and ultimately, diminished production as a mechanism to reduce loss and wastage.
The result is that local companies make a very low turnover rate, lowering the revenue of the host nation. Foreign companies that may be well funded may enjoy a large share of the local market since they might be well established and have more funding than the local companies. This makes local companies be at a competitive disadvantage and they may end up pulling out of business. The collapse of local industries promotes unemployment and high dependence levels hence, the government resources are converted from development expenditure into recurrent expenditure. Such a situation may lead a country into debts among other disastrous financial paths.
Globalization also promotes peace, democracy, and environmental cooperation among nations leading to formulations of agreements and pacts such as Montreal Protocol, Kyoto Protocol, and the several Strategic Arms Reduction Treaties13.
Globalization may also cause the collapse of local industries due to the creation of an imbalanced and unfavorable business environment. Due to the entry of new businesses into an already full economic setting, local industries may experience a shortage of factors such as labor, raw materials, and finance. Financial institutions may prefer to give findings to well-established and promising companies that may deny the developing local companies the chance to grow.
Besides, most foreign companies have better technology and are more appealing to the labor force than local industries. The high number of unemployed people leads to low living standards and a general feeling of insecurity that discourages entrepreneurs from setting up businesses and promoting crime. Due to the setting up of businesses in very many regions, there has been increased destruction of natural resources and the general environment.
These natural resources are the raw material for several crucial economic activities hence due to this damage; raw materials needed for the manufacture of some items have slowly been depleted. Immigration has caused ethnic and racial conflicts in several regions14. For example, in South Africa, there has been a nationality conflict with the locals accusing the immigrants of causing the high rate of unemployment the feud was so bad that most of the immigrants fled back their countries in fear of being killed or mutilated like their friends. The effect of these conflicts is that during the violence, economic activities are almost grounded.
Hence, the revenues generated at the time are reduced. Also, the host country is deprived of skilled manpower. Racial discrimination as witnessed in several regions of the United States of America and Europe is also a negative effect of globalization. This discrimination lower morale of immigrant employees from delivering and they are often looked down upon and treated harshly by society. If these immigrants were treated better, the economy would likely have a significant rise.
As seen from this paper, globalization carries with it a lot of benefits and challenges as well. These benefits affect every aspect of the world, but more so the economic status and development of the world. In 2012, “the world was made up of three billion workers, with over two hundred million people unemployed”15. The globalization, the methodology can be used to lead the world into global economic success, but this requires keen planning and law-making to ensure the process of succeeding does not ultimately lead to future conflicts.
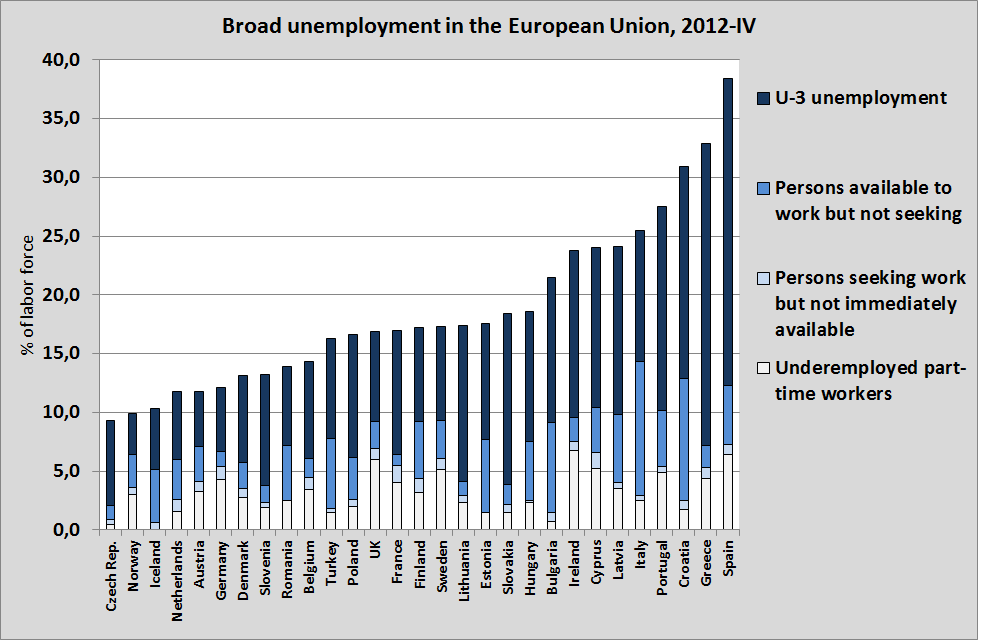
The graph above shows the employment trends in developed countries16.
Reference List
Appadurai, Arjun. Modernity At Large. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1996. Print.
Bhagwati, Jagdish. In Defense Of Globalization. New York: Oxford University Press, 2004. Print.
Oatley, Thomas H. International Political Economy. New York: Pearson/Longman, 2008. Print.
Robertson, Roland. Globalization: Social Theory and Global Culture. London: Sage, 1992. Print.
Sassen, Saskia. Globalization and Its Discontents. New York: New Press, 2008. Print.
Seay, W. “The origins of political Economy.” Lecture at Virginia Commonwealth University, Spring 2016.
Todaro, Michael and Stephen Smith. Economic Development. Boston: Pearson Addison Wesley, 2006. Print.
Footnotes
- W Seay, “The origins of political Economy,” (Lecture at Virginia Commonwealth University, Spring 2016).
- Thomas Oatley, International Political Economy (New York: Routledge, 2015), 23.
- W Seay, “The origins of political Economy,” (Lecture at Virginia Commonwealth University, Spring 2016).
- Ibid
- W Seay, “The origins of political Economy,” (Lecture at Virginia Commonwealth University, Spring 2016).
- Ibid
- W Seay, “The origins of political Economy,” (Lecture at Virginia Commonwealth University, Spring 2016).
- Thomas Oatley, International Political Economy (New York: Routledge, 2015), 23.
- Jagdish Bhagwati, In Defense of Globalization (New York: Oxford University Press, 2004), 18.
- Saskia Sassen, Globalization, and its Discontents (New York: New Press, 1999), 44.
- Poland Robertson, Globalization: Social Theory and Global Culture (London: Sage, 1992), 29.
- Saskia Sassen, Globalization and its Discontents (New York: New Press, 1999), 44.
- Jagdish Bhagwati, In Defense of Globalization (New York: Oxford University Press, 2004), 8.
- Roland Robertson, Globalization: Social Theory and Global Culture (London: Sage, 1992), 23.
- Arjun Appadurai, Modernity at Large (Minnesota: University of Minnesota Press, 1996), 67.
- Michael Todaro and Stephen Smith, Economic Development (Boston: Pearson Addison Wesley, 2006), 168.