Introduction
Small and medium enterprises play a significant role in the global economy by contributing to the commercial sustainability of nations. New entrepreneurs are ambitious individuals who enter the corporate domain intending to close an existing business gap. SMEs account for most employment opportunities and contribute to the national GDP. SMEs are undoubtedly the major contributors to the global economy.
Similarly, new entrepreneurs are part of global economic growth, and their success results in a stable and sustainable society. However, new entrepreneurs and SMEs have been facing challenges, lowering their chances of survival in the competitive business landscape. This study analyses the factors that lead to failure among SMEs and new entrepreneurs and offer suggestions on how to improve them to make them succeed.
Background of the Study
The principal role of entrepreneurs is to locate business opportunities and obtain the necessary resources to start and run a business to close the market gap. Entrepreneurs who are new in the market face numerous challenges which jeopardize their chances of success. An entrepreneur’s success is defined by the ability of the business to thrive and remain relevant in the market niche. Passionate capitalists drive small and medium enterprises to make profits (Hair et al., 2019).
However, most of the SMEs and new entries into the market fail to stand the test of time as they are prone to fail. It is imperative to note that passionate leaders manage start-ups with a burning desire to compete with existing and established firms (Yasin et al., 2021). The corporate lens on entrepreneurship requires new entrants into the market to conduct holistic research on the factors affecting business success. Many entrepreneurs are fascinated when starting businesses but must be cognizant that the trade sphere is dynamic and must be understood for survival.
Problem statement
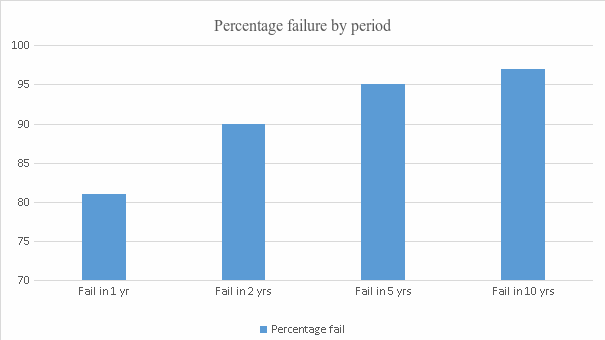
Governments worldwide support entrepreneurs by setting up financial policies to encourage them to generate revenue. Other support accorded to the entrepreneurs by governments include tax holidays and grants to increase their financial abilities. As entrepreneurs start their businesses, they aim to make profits and build a successful venture. However, research by Aminova & Marchi (2021) indicated that 90% of all new start-ups fail within five years of operation (p.41).
Numerous reasons that lead to their failure include lack of innovation and competition from existing firms. Although globalization opens numerous opportunities for businesses to thrive, failure to conduct a thorough will likely lead to business failure. Entrepreneurs and SME managers must understand all the challenges involved in small businesses and avoid them for business success.
Purpose, Objectives, and Concept Maps of the Study
The purpose of the research is to explore the reasons why SMEs and start-ups fail in the global corporate domain. When the reasons for failure are identified, it will be possible to plan the necessary strategies to overcome the challenge and reduce the failure rate. The research is guided by two main research questions, as shown below:
- What are the most common failure reasons for SMEs?
- How can SMEs succeed, and what are the critical success factors?
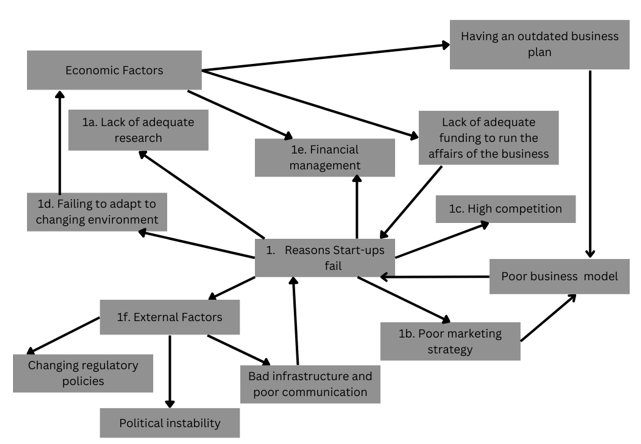
The typical failure reasons can be subdivided into numerous factors, as shown in the concept map presented in figure 1. The failure reasons may be explained as economic, social, political, or management plans. Under economics, the analysis will investigate the financial management, business planning, lack of adequate funding, and inability to cope with the dynamic company realm. The external reasons for failure may also be broken down into political instability, regulatory policies, and poor infrastructure (Aram & Salipante Jr, 2003). Although there are numerous internal and external factors, the critical objective is identifying the factors most likely to make new businesses and SMEs fail and proposing recommendations to improve business conditions. The main factor contributing to most start-up failures will be identified in the long run.
The critical success factors for business success will also be categorized and analyzed for the entrepreneurs to know which factors are the most crucial for business success. The critical categories analyzed for the critical success factors include financial, management, research, and managing competition. Investing in disruptive technology will also be discussed, as how it contributes to success factors in the business realm (Christensen & Raynor, 2003). The main goal of the second analysis is to determine the exact factors that must be applied for a business to succeed in the discourse.
Research Rationale
The primary rationale for conducting the research is to answer why most start-ups fail in the business realm. The answers will be determined by conducting a primary survey on the entrepreneurs and further probing why start-ups fail from secondary research (Hair et al., 2019). Further, the study will investigate the key factors that can be implemented to enhance business success (Facchini et al., 2021). The research results will lead to developing recommendations aligned with the success factors. Therefore, this study is an essential handbook for investors, entrepreneurs, and financiers to make the necessary business decisions and apply the factors that enhance business success in the long run.
Limitations
Research limitations are all factors that tend to affect the overall outcome of a study. Since the research aims at identifying the causes of failure in SMEs, a successful researcher must have background information about running businesses. A lack of previous financial or business knowledge may affect the ability to critically analyze the data produced in research. Further, the study focuses only on start-ups and SMEs in the commercial domain, which may limit the scope of data available in the search engines. Another critical limitation is bias and false information encountered during the data collection. Bias, false information, and limited research scope may jeopardize the overall quality of the research. The investigator must therefore look out for the limitations during the study to ensure an effective outcome in the long run.
Literature Review
Introduction
A literature review is an integral part of research because it offers the framework for guiding the research. The key points raised in the literature review will likely shed more light on the research questions and broaden the scope. A reader will therefore be able to place the study in its relevant context and help understand the challenges affecting small businesses. The research further places the theoretical framework that can be used to understand the business concept.
Major Factors Leading to SMEs and New Entrepreneurs’ Failure
The typical failure reasons associated with business failure may be categorized as either internal, external, economic, or environmental factors as broken down in the concept map. A detailed analysis from secondary research showed numerous factors that contribute to business failure in the discourse. Research by Alnassai (2023) showed that entrepreneurship is the typical source of employment globally and is encouraged globally for people to survive. However, six key reasons can be described as the key sources of failure in the business realm (Aminova & Marchi, 2021). Financials, leadership, regulation, competition, poor business plan, and lack of innovation are the key aspects that lead to failure in SMEs and start-ups.
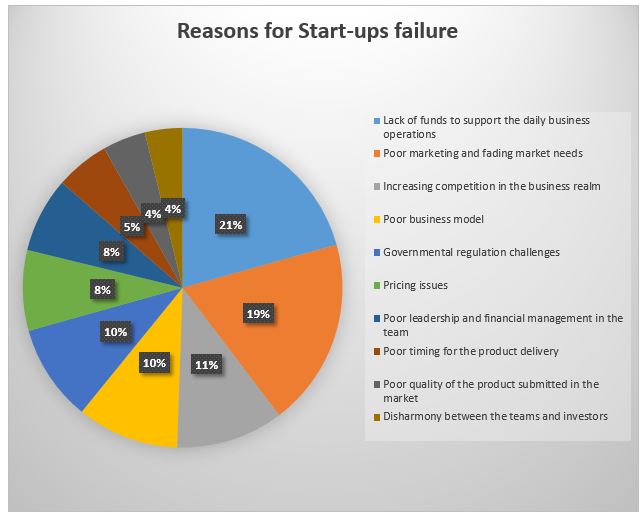
Appendix 1 and 2 show the significant reasons that constitute business failure. Due to the multiple reasons associated with the failure of small business and new entrepreneurs, some businesses shut at different times. Table 1 in the appendix shows the percentage of businesses that fail within two, five, and ten years. Figure 2 shares the graphical representation of the closed businesses over time. Further, table 2 summarizes the common reasons that lead to the failure of businesses. Figure 3 shows a pie chart summarizing the reasons for business failure.
Financials
Financial factors constitute one of the significant reasons why SMEs and start-ups business fail. Some of the businesses require higher capital for investment. A person entering the market with limited capital may fail to sustain their operations, leading to failure. According to Gelderman et al. (2021), 34% of small businesses that fail are due to financial challenges (Aminova & Marchi, 2021). The financial causes may take a broad spectrum ranging from less capital, higher rent requirement, and salaries paid to the staff. The financial hurdles are key reasons why most start-ups fail before they have a chance to thrive.
Leadership
Leadership is an essential factor in business success as they close opportunities in the market. Leadership is a holistic challenge that affects small businesses and limits their ability to make timely decisions. A good leader continuously analyses the situation and makes decisions aligned to success (Aram & Salipante Jr, (2003). For example, a good leader of an SME motivates the employees to work well and offers team leadership on all the factors that need collaboration to be achieved. Organizing resources effectively amounts to poor leadership in the business domain. Research by Eisenhardt & Graebner (1989) offered a similar outcome that poor leadership is the prerequisite for the failure of small businesses. Investors and entrepreneurs with poor leadership skills are prone to fail compared to other businesses.
Regulations
Government regulations play a crucial role in SME and new entrepreneurship performance. Facchini et al. (2021) researched the impact of government regulations on start-up failure. The research inferred that over 22% of the failed businesses are accredited to the unfriendly regulations by the government. Whereas nations promoting tax holidays for new businesses tend to improve their performance, over-taxation is a crucial regulation parameter that leads to death in the long run. Further research by Lallé (2003) showed that unfavorable governmental regulations are the main reasons small businesses fail to thrive.
Competition
Competition is one of the main reasons why start-ups fail. As a new business enters the market, it is prone to face competition from established firms that have a clear understanding of the market dynamics. The trade experience exhibited by investors who have been in the business for a long may lead to failure in the discourse. The study by Lallé (2003) further concluded that competition is a leading factor of failure in the long run. Investors who do not analyze the competitors before venturing into the business will likely fail in the long run.
Poor Business Planning
Business planning is an essential aspect of constituting and running a business. A business plan is a document that shows how management must perform its operations for success. Research by Facchini et al. (2021) proved that poor business planning leads to most business failures, especially start-ups. Investors with poor business planning skills may lead to business failure in the discourse. However, research by Eisenhardt & Graebner (2007) stated that poor business planning is not one of the major causes of small business failures.
Innovation
Innovation is the ability of investors and other business people to create unique solutions to challenges affecting the customers in the discourse. A study by Aminova & Marchi (2021) found that the corporate realm is dynamic and always requires business people to innovate and change the study’s outcomes. Failure to innovate can be attributed to numerous factors in the business realm, such as motivation levels and having a manageable work load at all times.
Critical Success Factors for SMEs and New Entrepreneurs
The research intends to determine the main factors that can be applied to overcome business failure. When the investors understand the reasons for failure, it is possible to convert the limiting factors to the most successful factors that may be used to overcome the challenges in the discourse. Critical factors for success in the corporate domain include research and development, proper financial management, innovation development, and appropriate government policies.
Proper Financial Knowledge and Management
Financial hurdles are some of the most crucial challenges that affect the day-to-day running of businesses. Since financial issues are the fundamental causes of business failure, acquiring the necessary knowledge makes it possible for a person to navigate the financial realm to make better decisions. According to research by Eisenhardt & Graebner (1989), attaining the appropriate financial knowledge is the antidote for business success. Investors must therefore invest in financial management or consult the expertise to make the most important financial decisions.
Research and Development
Research and development is an emerging trend in the business environment which allows investors to be in touch with the customers’ needs and customize the goods to match their needs. Since one of the reasons for failure is the inability to cope with a changing financial realm, small businesses must incorporate research and development in the business realm (Polonsky & Waller, 2015). Research and development increase success in the business environment by instilling innovation in entrepreneurs. A study by Christensen & Raynor (2003) inferred that understanding the customers’ needs is the key to increasing creativity in solving the customer’s problem. Setting aside resources for research is, therefore key to
Appropriate Government Policies
SMEs and new entrants to the market all serve as a source of revenue to the government through taxes. Therefore, the government’s role is to ensure that businesses are always protected. Aram & Salipante Jr (2003) inferred that nations with appropriate government policy experience lower start-up failure rates compared to nations with poor government regulation policies. Since globalization allows people to invest in the places of their choice, investors can choose countries with appropriate regulatory policies for a better business environment.
Adequate Market Research and Analysis
Market research is important to beat corruption in the competitive trading realm. Since competition is termed as one of the most challenging SMEs and new entrepreneurs. Whenever the company conducts adequate market analysis, it will understand the market dynamics (Lee & Lings, 2008). Alnassai (2023) inferred that when an entrepreneur conducts adequate market research and analysis, they will likely make more profits in the long run.
Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework explains the research objectives and how they can be achieved through different models. Two critical theories inform the reasons for start-up and SME failure. The self-justification and Drucker theory help us understand the decision-making models used in running businesses (Aminova & Marchi, 2021). When a person understands the theories, they are likely to make informed decisions concerning investment, regulations, and management.
Self-Justification Theory
The self-justification theory explains the self-confidence exhibited by entrepreneurs as they formulate business ideas. However, justifying their ideals without aligning them with the corporate policies may lead to failure (Aminova & Marchi, 2021). Leon Festinger coined the theory to explain how cognitive dissonance affects a person’s internal consistency and therefore fails to make accurate decisions in the corporate domain (Alnassai, 2023). When the change occurring in the market is not aligned with the entrepreneur’s internal consistency, it may lead to business failure. When investors understand the theory, they become more acquainted with making decisions that are good for the business regardless of their internal consistency.
Drucker Theory
Entrepreneurs must have a change framework to help them align their decisions to the ever-evolving professional landscape. An entrepreneur coined the Drucker theory to explain how people should react to changes in the business arena (Drucker, 2020). According to the theory, a successful entrepreneur must clearly understand the business dynamics, laws, and policies before making decisions to run a business. Once a person understands the changes in the business, they are likely to succeed (Putra & Cho, 2019).
As the study evaluates the reasons for business failure and probes to determine the solution, the Drucker theory helps businesses to overcome challenges. The theorist focused on innovation and adequate marketing as the antidote for business success (Gelderman et al., 2019). Applying the theory is key for successfully implementing unique features in the corporate landscape.
Research Methodology
Introduction
This chapter is crucial to the overall project because it allows the researcher to collect and analyze primary data for effective action. Since the research’s primary purpose is to determine why start-ups and SMEs fail, the methodology involves reaching out to the investors who failed (Davis et al., 2007). Feedback from the participants helps to obtain firsthand information on why the business failed. The feedback will further formulate the best ways to overcome the challenge.
Research Design and Reaching Out to the Participants
The participants were selected from convenience sampling where referral links were sent via social media domain. Interested participants were registered and data collection made possible at their expediency. The conducted study was descriptive, exploratory, and qualitative. The method is selected because it offers the researcher insight into understanding and using a phenomenon to get better outcomes in the discourse.
According to Aminova & Marchi (2021), qualitative research is the antidote for understanding phenomenon and relationships and offer a chance for the researcher to learn from the participants. This qualitative study was conducted online using surveys and interviews to interact with business owners and collect information on reasons for failure. The use of technology was vital in the collection and sampling of data. Appendix 3 is the consent letter signed by the participants as a manifestation of ethical research process. Appendix 4 shows the predetermined questions that were answered by the participants.
Research Methodology
The research methodology shares the specific procedures and techniques used to obtain and process data to obtain information. This research used two data collection methods to obtain data from the affected people. A survey is a research strategy where the selected participants are asked a series of questions, and their feedback is collected (Alnassai, 2023). A digital survey was conducted through the online platform where requests were made on the online domain to ask people who had been in business to share their ideas. Other than the online surveys, interviews were also conducted via zoom to collect data face-to-face.
A population of 45 was taken through the online survey, where they were offered an online questionnaire with pre-prepared questions. The research questions sent to the participants are attached in the appendix. Ten other participants were taken through a 30-minutes interview via zoom. It is prudent to note that each individual had to sign a letter of consent to ensure that they were willing to participate in the data collection. The consent letter is also attached as proof of ethical practice. The data collection procedure ensured that the personal and professional opinions of the participants were received in the long run.
Data Collection Population and Sampling
Data sampling during research is as important as the collection since poor data analysis leads to wrong results. Data was collected through online platforms where 45 participants filled out an online Google form and uploaded it to a password-controlled database. A total of 55 participants participated in the study, and their records were transmitted electronically and downloaded as hard copies for analysis. The zoom meetings were also recorded as videos which were retrieved for analysis. A thematic analysis placed data in the correct cluster themes for easy understanding. For example, the first process involves reading through the answered questionnaires and then gathering separate themes on the reasons for business failure in the long run. The thematic analysis yielded the results that are analyzed in chapter four.
Results and Discussion
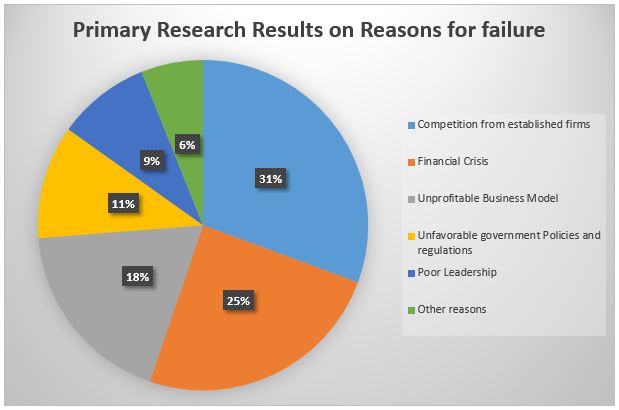
The primary aim of the research was to obtain the causes of business failure and determine the main strategies to overcome the challenges faced by the business and ensure that they are successful. The clustered data showed four of the six major causes of business failure. Understanding the causes of failure is the prerequisite for determining solutions for a better outcome. Competition from established businesses was the most pertinent cause of failure in the SMEs and new entrants into the information. The reasons for failure are arranged from the most pertinent to the slightest cause of business failure.
Competition from Established Firms
Although the respondents gave different view causes as to why their businesses failed. The high competition was mentioned by 50 out of the 55 respondents as the leading cause of failure for small businesses. When a person enters the market as a new trader, other traders have been in the industry for a long. The competitors have enough understanding of the market dynamics. In the opinion sections, the respondents stated that they failed to recognize red flags which were evident to their competitors. Further, competitors of the new entrants had all the information about the market, and newbies could only compete when they collected enough data.
One of the most apparent reasons the new entrants into the market cannot beat the older businesses is the customer loyalty the competitors have built over the years. For example, when entering the fashion industry, some brands like Nike, Gucci, and others have built their brand image. It is imperative to note that SMEs and new entrepreneurs must conduct a thorough market analysis and develop a new strategy that meets the needs of the business.
Financial Crisis
Financial constraint is the second biggest challenge that affects business industry people and prevents them from succeeding in the venture. Since some investments require higher capital, the new entrants may need more resources to overcome the challenge. 40 out of the 55 respondents cited financial constraints as one of the reasons for failure in the business realm. When people plan to enter business, they are always enthusiastic and optimistic about making profits.
Some pay rent for the first three months, hoping it will have broken even and started covering the bills. However, financial uncertainties lead to losses, and small businesses must shut down (Alnassai, 2023). Further, poor financial decisions are the principal cause of failure. In some cases, entrepreneurs need more basic accounting knowledge, and unprofessional accounting practices lead to losses and failure in the long run.
Unprofitable Business Model
Most business models are planned based on the market gap existing for investment. Although leadership failure was pointed out in the interview, most survey respondents agreed that unprofitable business models and failure to appeal to the customer were one of the causes of failure in small businesses (Miles, 2019). 30 of the 45 respondents stated in the reviews stated that when the business model selected does not appeal to the customers, it led to the failure of the business.
The strategies to overcome the challenge were to conduct solid market research, understand the customers’ needs and then develop different models. Research by (Alnassai (2023) indicated that 80% of customers would be willing to buy from a new entrepreneur only if there is a huge design innovation. Whenever new entrants in the market need more innovation and differentiation of the products, they are likely to fail in the discourse.
Unfavorable Government and Regulation Policies
SMEs and other new entrants have to pass through the regulatory bodies to ensure sustainable development and economic feasibility. Since the regulatory bodies view SMEs as sources of revenue, higher taxes are likely to discourage SMEs and new entrants from thriving in the corporate domain. Eighteen of the participants in the study revealed that their businesses ended because they were frustrated by the higher taxation before the business could stabilize.
The government policies must therefore be favorable for the businesses to thrive. Businesses must therefore understand all the external environment, such as taxes and regulatory authorities, to make decisions aligned with the regulatory expectations for success. They are likely to fail whenever new businesses are ambushed with new taxes and dues before they stabilize. Far sited government must therefore ensure that they set favorable economic policies for the businesses to thrive.
Poor Leadership in the Business Realm
Leadership is essential to the business’s day-to-day running, such as faster decision-making. Decision-making is a crucial factor when people face challenges in the business world. 15 out of the 55 respondents stated that they failed in their businesses because they made untimely decisions that led to the failure in the discourse. Therefore, new market entrants must ensure they have the right leadership skills to form alliances whenever necessary and resolve all the challenges in the long run. Investors must therefore ensure they have all it takes to evaluate information and make urgent decisions for success. Appendix 5, figure 4 and table 3 summarizes the reasons for business failure. The other reasons for failure include pricing issues and wrong timing among others.
Conclusion and Recommendation
The research’s final chapter summarizes the primary and secondary data to deduce the leading causes of business failure and help formulate strategies to overcome the challenge. Integration of the findings and secondary research is critical for developing the critical solutions to the problems (Miles, 2019). The final chapter offers recommendations for new entrants to determine the best outcomes for their businesses to thrive.
Conclusion
Competition from established firms is the leading cause of failure for small enterprises and start-ups. Since the established companies have a large customer base. As the new business enters the market, it must have access to the information regarding its competitors and make it possible to deliver services aligned with the customer’s needs. Financial challenges and failure to meet customer expectations are other causes that have made start-ups fail to thrive. People can enter new markets after conducting adequate research in the long run. Unhealthy regulatory bodies and evolving corporate domains are other key causes for the failure of small businesses in the long run.
Recommendation
After analyzing the causes of business failure, the following recommendations were given to make work more effortless in the corporate domain.
- New entrants must conduct a market analysis, understand the market dynamics and enter it only after understanding the competitors. Once the businesses understand their competitors, they can introduce new products and services that are unique and meet the customers’ needs at all times. Further, an active research and development department must always be present to inform management of business issues. When a research and development department is formed, it will help the business to be in touch with the changing business environment this enabling it make the necessary decisions whenever needed. Further, the investors must learn more about emotional intelligence to maintain a positive relationship with customers and other stakeholders.
- Business modelling is a holistic process where an investor understands the market, identify the gap, and investigate all the anticipated expenses to make profits. In the process of business modelling, all the market dynamics will be understood and covered in the problem-solving process. A poor business model jeopardizes the chances for success hence leading to business failure in the discourse. The investors must therefore seek the services of professional business accountants to create a business model that offers customized solutions to customer challenges.
- Professionalism and leadership are essential values that new investors must have as they enter the market. Most financial blunders are committed because the new entrants need more financial education to overcome. The new entrants need to have the correct leadership and professional skills. Innovation increases marketing, and disruptive technology may lead to success. Finally, a regulatory and external policies analysis must be considered when investing in a business.
References
Alnassai, J. M. I. A. (2023). A study on the barriers to entrepreneurship in the UAE. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 16(3), 2-14. Web.
Aminova, M., & Marchi, E. (2021). The role of innovation on start-up failure vs. its success. International Journal of Business Ethics and Governance, 4(1), 41-72. Web.
Aram, J. D., & Salipante Jr, P. F. (2003). Bridging scholarship in management: Epistemological reflections. British Journal of Management, 14(3), 189-205. Web.
Christensen, C. M., & Raynor, M. E. (2003). Why hard-nosed executives should care about management theory. Harvard business review, 81(9), 66–75.
Ciloci, R. (2022). The causes of small businesses failure. Journal of Social Sciences, 2(5), 131-142. Web.
Davis, I., Keeling, D., Schreier, P., & Williams, A. (2007). The McKinsey approach to problem-solving. McKinsey staff paper, 66-69. Web.
Drucker, P. F. (2020). Peter F. Drucker on the Network Economy. Harvard Business Press.
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Graebner, M. E. (1989). Theory building from case study research. Academy of management review, 14(4), 532-550. Web.
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Graebner, M. E. (2007). Theory building from cases: Opportunities and challenges. Academy of management journal, 50(1), 25-32. Web.
Facchini, F., Jaeck, L., & Bouhaddioui, C. (2021). Culture and entrepreneurship in the United Arab Emirates. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 12(1), 1245–1269. Web.
Gelderman, C. J., Mampaey, J., Semeijn, J., & Verhappen, M. (2019). Self-justification for opportunistic purchasing behavior in strategic supplier relationships. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 34(2), 451-462. Web.
Hair, J. F., Page, M., & Brunsveld, N. (2019). Essentials of business research methods. Routledge.
Lallé, B. (2003). The management science researcher between theory and practice. Organization Studies, 24(7), 1097–1114. Web.
Lee, N., & Lings, I. (2008). Doing business research: a guide to theory and practice. Sage Publishers, London.
Miles, D. A. (2019). Research methods and strategies: Problem statement development: How to write a problem statement in a dissertation. In Workshop: Confessions of a dissertation chair part (Vol. 1, pp. 26–29).
Polonsky, M. J., & Waller, D. S. (2015). Designing and managing a research project: A business student’s guide. Sage Publishers, London. Web.
Putra, E. D., & Cho, S. (2019). Characteristics of small business leadership from employees’ perspective: A qualitative study. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 78, 36-46. Web.
Yasin, N., Khansari, Z., & Tirmizi, K. (2021). Exploring the challenges for entrepreneurship business incubator hubs in the United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Globalisation and Small Business, 12(2), 190-212. Web.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Percentage of SMEs failing with Time
Table 1 – Percentage of SMEs failing with time.
Appendix 2: Reasons Why Start-Ups Fail Worldwide
Table 2 – Reasons for SMEs’ failure.
Appendix 3: Consent Letter
I…agree to take part in this research, having been made to understand all the general purposes and the methods to be used. Although the research may not directly impact me, I agree to share my experience to help other people who want to venture into entrepreneurship. My participation is purely voluntary, and I have participated without being forced or coerced.
Signature…
Date…
Appendix 4: Interview Questions for both the online survey and face-to-face interview
Part A: Personal Details
- Name… (Optional)
- Age… (Optional)
- Gender… (Optional)
- Country of Residence… (MANDATORY)
Part B: Reasons for Failure
- How long did your business run?
- What was the key reason for the failure?
Part C: Recommendations
- What mistake did you make in your business?
- What do you recommend to help others succeed in their business going forward?
Additional comments.
Appendix 5: Results of the Primary Research
The results of the primary research were simplified into five major categories as shown in the table and the table and graph below. It is further imperative to note that the next column for others shows other reasons other than the five main reasons.
Table 3. Reasons for business failure from the primary research.