Introduction
Performance is the real determinant for survival and success in the marketplace. High-performing employees are associated with great achievements. In addition, they help their employer to gain a competitive advantage over rivals. According to Becker, Huselid, and Ulrich (2001), excellent performance is what creates a difference between great corporations and average firms. To ensure success, it is important for organizations to develop systems that recognize, retain, and remunerate top performers in the workforce.
The aim is to attain substantial growth in the industry. Firms in today’s corporate world invest large sums of money in efforts to acquire performance management systems. The major objective of such systems is to facilitate growth. In spite of these investment efforts, variation in employee performance continues to be a major problem in most companies (Aguinis 2012).
Performance management system is a structure that is used to facilitate the attainment of both organizational and individual goals. The systems help managers to monitor and track the level of work and performance among departments, individual employees, and the entire company. Aguinis (2012) is of the opinion that these performance management systems are often based on job and core organizational competencies. The competencies need to be attained to ensure the success of the firm. The primary components incorporated into the systems include individual development plans, accomplishments, and goals and objectives. Others are supervisor ratings and feedback results.
In this paper, the author will develop a performance management system for Procter and Gamble. In addition, the writer will suggest improvements to the existing PMS in the company. The recommendations to enhance the system will be based on literature review and sound practices with regards to PMS.
Procter and Gamble: An Introduction
Overview
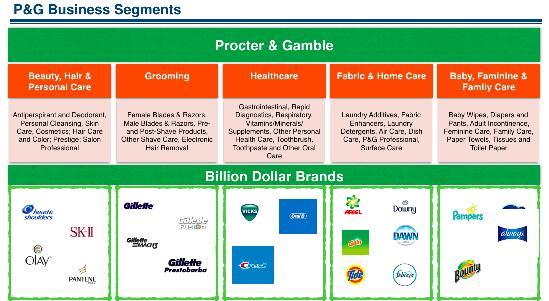
Procter and Gamble Company (P&G) was formed on May 5, 1905. The corporation specializes in the manufacture and distribution of different packaged products (DeLong et al. 2005). Some of the main goods produced by the organization include those targeted at the beauty, grooming, healthcare, fabric, and home care markets. Others are baby, feminine, and family care products. The global operations of the firm are overseen by the company’s Sales and Market Operations (SMO) department.
The two branches are responsible for the establishment and implementation of market plans at the local level. The SMO is made up of devoted retail consumer business channels and country-specific teams. To better understand the market and provide high quality services to the customers, P&G makes use of GBS technology processes and data tools (Everyday changes that make a world of difference 2016). Appendix 1 is an illustration of the company’s products.
Current Performance Indicators
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurements used to evaluate the success of a company. For managers to choose the right KPIs, they must have a good understanding of what is essential to the organization (Fitz-enz & Davison 2002). The indicators used by P&G are based on the reviews received from employees, supervisors, and students. The Senior Vice President of the HR is charged with the responsibility of overseeing the annual diversity reviews with the directors and management teams of each department.
The performance of employees is reviewed based on such aspects as their abilities and attitudes. On its part, the evaluation of supervisors is based on their ability to develop workers regardless of their sex and age (Everyday changes that make a world of difference 2016).
Unexpected and Undesired Problems
Procter and Gamble has achieved long-term success over the decades. However, the company faces a number of challenges. The key problems include those related to performance, continuous pressure to innovate, changes in customer dynamics and preferences, and environmental sustainability (Grant 2014). Other challenges include the execution of emerging market strategies, competitive intensity, and decisions about the brands to maintain.
An Outline of the Performance Management System Plan
Employees need guidance, oversight, and reviews on a regular basis. The reason for this is to help them know what is expected of them. In addition, the procedure enables them to work smart and improve their performance. Hammer (2007) is of the opinion that companies with effective performance management systems experience high levels of productivity. In addition, they identify top performers and ensure that their strategic organizational goals are in line with their development and recruitment procedures. The figure below is an illustration of a conventional performance management system cycle:
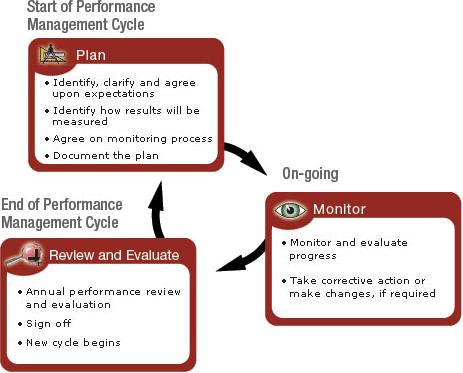
To develop a performance management system for Procter and Gamble, a number of issues will be taken into consideration. The facets include groups or types of jobs in the company, the stakeholders who provide feedback, and performance constraints (DeLong et al. 2005). It is also important to look into when and how often appraisals should be carried out, integration with other HR processes, training and instruction, and privacy and confidentiality of the results generated.
Job Groups
The design and process of performance management systems vary depending on job groups (Varma, Budhwar & DeNisi 2008). Executive jobs, for example, have goal-based systems, which are complemented by the evaluation of core competencies. On their part, project-oriented works have objectives-based systems. The systems are related to the plans of a given project.
Source of Feedback
The process of determining people who provide feedback on employee performance varies depending on the goals of the procedure and the nature of the job (Giangreco et al. 2010). The system proposed for P&G will incorporate feedback from a wide range of sources. The identified stakeholders include supervisors, managers, and clients.
When and How Often to Appraise
Performance evaluations will be made by considering a number of factors. The facets include project cycle, anniversary date, and business year (Grant 2014).
Training and Instruction
Performance management is a challenging process for most organizations (Shields 2007). When developing a system for P&G, training and information sessions for both employees and managers will be organized. The primary objective of these meetings is to help these stakeholders understand the system and benefit from it.
Confidentiality of Results
Privacy and confidentiality is essential when dealing with feedback from employees (Giangreco et al. 2010). To this end, a channel will be developed to determine the persons with access to the end results. In addition, measures will be taken to store the data in a secure place.
Essential Performance Criteria and Measurement
Essential performance criteria are analytical reports that document what is to be evaluated and the required level of performance. The statements specify the sets of skills, tasks, understanding, and knowledge that are essential in proving competence and performance. According to Aguinis (2012), performance criteria help managers to determine the most performing employees and workers who need more training and support.
Performance at P&G can be measured by taking into consideration a number of factors. The elements include quality of work, attitude, punctuality, personal presentation, random checks, and client survey (Hammer 2007). Punctuality as a means of measuring performance entails checking employees who arrive late or those who are absent on a regular basis (Behery & Paton 2008). Such individuals are unlikely to attain their performance objectives. Absenteeism and punctuality concerns prevent workers from actualizing their full potential.
Quality of work is a key aspect in measuring performance. Determined and engaged employees are more productive and perform better. In addition, their tasks match the required standards. To determine quality, managers at P&G should assess whether a given work is of average or outstanding level (Grant 2014).
Attitude towards work will influence the performance of individuals working for P&G. Hammer (2007) observes that employees with bad outlook towards their jobs perform poorly. In addition, such workers fail to comply with organizational policies. Client surveys measure performance through feedback. Fitz-enz and Davison (2002) are of the opinion that poor performance manifests itself through customer service. It is expected that satisfied employees at P&G will offer positive responses. The feedback means that their performance is meeting the expectations of the customers.
Key Recommendations
The primary elements of performance management process at P&G are learning and focus. The aspects are essential in motivating employees to take part in organizational duties. However, to ensure the issue of performance is well addressed, the corporation’s management should focus on different elements that will enhance motivation of the workforce. The following are the key recommendations with regards to the proposed performance management system plan:
Connecting Employees
It is recommended that managers at P&G should develop and organize activities that will connect employees from all levels in the organization. One way of bringing workers together is by organizing gatherings and parties where all employees are invited (Varma, Budhwar & DeNisi 2008). Such occasions improve relationships between employees and managers. The developments can influence teamwork and enhance performance.
Compensation and Benefits
Another recommendation entails compensations and benefits. The two elements impact on motivation and productivity among employees. Procter and Gamble should realize that workers who are rewarded as required for their job will strive to work harder and achieve more success (Shields 2007).
Communication
The third recommendation involves communication (Shields 2007). Procter and Gamble should organize a series of meetings, conferences, and seminars. Such events help employees to better understand the business and what they need to do to drive the company forward.
Adoption of the 360 Degrees Appraisal System
Procter and Gamble should consider adopting this appraisal system. The approach will involve a systematic method of collecting information on feedback and performance on an individual or group of employees (Shields 2007). The data gathered through 360 degrees will enhance the relationship between employees and managers in the organization.
Engage Workers in Decision Making Processes
To enhance performance and involvement of employees in organizational matters, P&G should engage workers in decision making. As a result, the workforce will feel appreciated and trusted (Becker, Huselid & Ulrich 2001).
Develop Improvement Systems
Organizations are made up of both high and low performing employees (Giangreco et al. 2010). To help underperforming workers and enhance productivity, P&G should develop improvement plans with a wide range of guiding principles. In addition, managers should ensure that such employees work closely with the supervisors. The aim is to help them learn more and receive guidance where necessary.
Expected Outcomes
The proposed PMS plan for P&G will have positive effects on individual employees, teams, and the organization at large.
Individual Employees
The PMS is expected to make the employees become self-motivated. The reason is that the system will ensure each worker understands what is expected from them. As such, they will work harder and smarter to attain their goals. According to Becker, Huselid, and Ulrich (2001), workers who know and understand their roles in an organization portray high levels of affectivity and efficiency.
The PMS will also improve self-learning and career development. Underperforming employees will be motivated to develop a positive attitude towards work. The change will play an important role in career development. The reason is that they will be more willing to learn and contribute towards the attainment of the organizational goals (DeLong et al., 2005).
Impacts on Teams
The application of PMS by P&G will foster teamwork and harmony between employees. It will bring together workers and managers, encouraging the development of a good and friendly working environment (Hammer 2007). When employees are free and comfortable with each other, they associate more and develop work groups and teams.
The PMS is expected to encourage sharing and brainstorming of new ideas. In addition, the system will promote cooperation and enhance communication in P&G. Individual employees have different ideas on how to tackle a problem (Varma, Budhwar & DeNisi 2008). To pick the best solution, individuals in the group will present their suggestions and evaluate the most appropriate alternative.
Impacts on the Organization
The adoption of the PMS by P&G is expected to increase developmental opportunities. In addition, it will make workers more committed to the organization (Grant 2014). Individual growth, self-motivation, and positive attitude towards work will help employees realize their full potential and achieve their goals. When workers are fully committed, productivity is enhanced, leading to improved organizational performance.
Measuring the Effectiveness of the PMS Plan
The effectiveness of the PMS will be measured by comparing the results achieved with the defined goals. Over the decades, P&G has strived to ensure organizational success by enhancing employee motivation. The proposed PMS plan can be measured through the SMART criteria. The figure below illustrates the use of the SMART criteria:
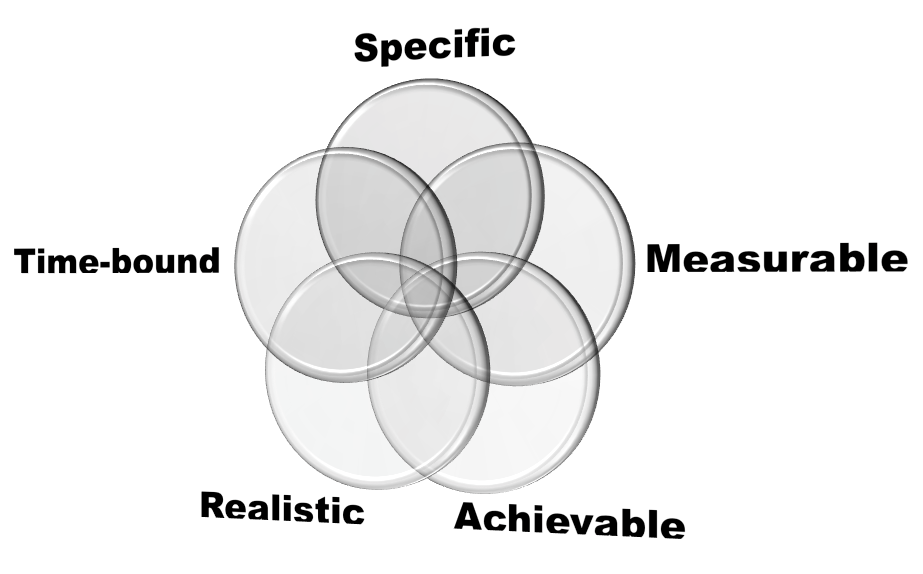
S-Specific Elements
A set of specific elements will be made clear to all workers (Shields 2007).
M-Measurable Goals
A set of measurable objectives will help the managers to determine what should be evaluated. The aim is to monitor the progress made towards the achievement of the set goals (Aguinis 2012).
A-Achievable Goals
The goals set will be achievable. They will help the management to develop new ideas regarding the desired objectives at P&G (DeLong et al. 2005).
Realistic Objectives
A set of realistic goals will be used to assess the capabilities of each employee after implementing the PMS (Aguinis 2012). The management will use this criterion to determine whether the objectives can be achieved through the available resources and knowledge or not.
T-Time Bound
The management will come with a duration that is enough for the achievement of the set objectives (Hammer 2007).
Conclusion
Contemporary corporations are striving to motivate employees, enhance productivity, and maintain a competitive advantage. Procter and Gamble can use the PMS proposed in this paper to improve and monitor the performance of employees and the firm as a whole. The management should realize that performance management entails more than just the provision of annual reviews for employees. The concept should focus on identifying the strengths and weaknesses of individual workers. The benefits associated with the effective implementation of the PMS include financial gains, improved accountability, open communication, and growth of employees.
References
Aguinis, H 2012, Performance management, 3rd edn, Pearson, Boston.
Becker, B, Huselid, M & Ulrich, D 2001, The HR scorecard: linking people, strategy, and performance, Harvard Business School Press, Boston.
Behery, M & Paton, R 2008, ‘Performance appraisal‐cultural fit: organizational outcomes within the UAE’, Education, Business and Society: Contemporary Middle Eastern Issues, vol. 1 no. 1, pp. 34-49.
DeLong, T, Brackin, W, Cabanas, A, Shellhammer, P, & Ager, D. 2005. Procter & Gamble: global business services. Web.
Everyday changes that make a world of difference. 2016. Web.
Fitz-enz, J & Davison, B 2002, How to measure human resource management, 3rd edn, McGraw-Hill Education, London.
Giangreco, A, Carugati, A, Pilati, M & Sebastiano, A. 2010. ‘Performance appraisal systems in the Middle East: moving beyond Western logics’, European Management Review, vol. 7 no. 3, pp. 155-168.
Grant, T 2014, International directory of company histories, St. James Press, Detroit, MI.
Hammer, M 2007, The 7 deadly sins of performance management and how to avoid them. Web.
Shields, J 2007, Managing employee performance and reward: concepts, practices, strategies, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Varma, A, Budhwar, P & DeNisi, A 2008, Performance management systems: a global perspective, Routledge, Abingdon.
Appendix
Appendix 1: The products of Procter and Gamble