Introduction
In recent decades, the telecommunications industry has been subjected to various high-level threats, each of which has resulted in significant financial losses. As a direct consequence of this, several telecom companies have been forced to shut down their activities. On the other hand, some people have been forced to pay enormous penalties due to the implications of losses sustained as a result of certain hazards. The Telstra Corporation is not an exception; it has found itself in the middle of a crisis numerous times over the years. As a result, it has been forced to pay fines of up to fifty million dollars owing to unfair marketing and sales practices. On top of all of that, Telstra was recently the target of a cyberattack, which resulted in disclosing sensitive information about the company’s customers. Consequently, this research looks at Telstra Corporation’s attempts to address a wide variety of industry hazards and operations, which are a source of contention in the telecommunications sector. In this article, Telstra presents its methodology, which may be followed step-by-step to ensure that the threat does not have any additional adverse effects.
Organizational Contexts
Telstra, much like every other company in the telecommunications sector, has been negatively impacted as a result of the industry’s exposure to a diverse variety of hazards. It is of the utmost importance to ascertain whether or not the company is ready to avoid future bad outcomes from causing damage to its operations, reputation, or profits. This article discusses Telstra’s risk management strategy to mitigate the dangers linked with the firm. It is of the utmost importance to ensure that the business can carry on with business as usual and without disruptions. Although risk management is universal, the success of the process depends on the participation of all stakeholders who are subject to risks that the telecom firm did not expect. Telstra wants to involve all of its stakeholders, including its employees and customers, in developing measures to protect it from the possible damage it could suffer due to its exposure to the implications of the risks. It is done to protect itself from the possibility that it could suffer this damage.
Risk Management Process
The proper management of risk necessitates the implementation of some procedures. In terms of risk management, there are five steps to the process that must be completed as illustrated in the figure below:
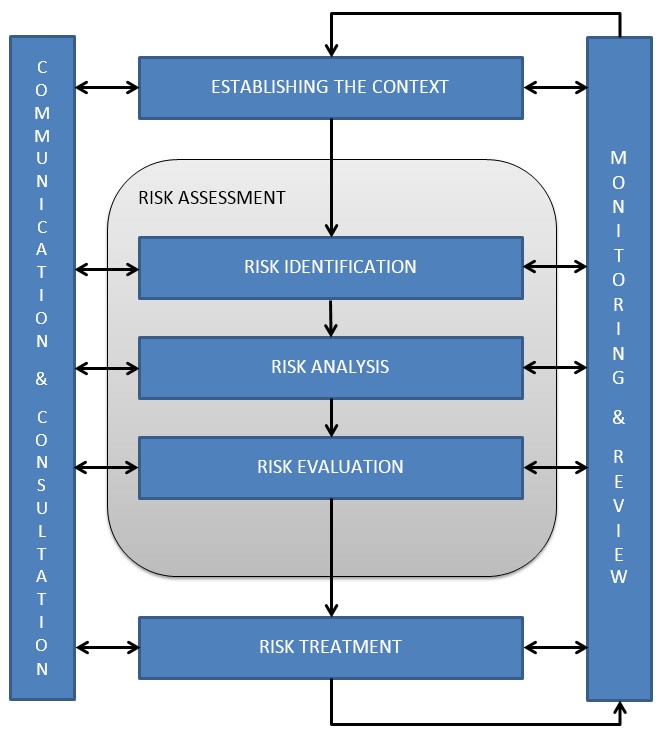
After identifying and prioritizing the dangers, the administration needs to develop a solution, and ultimately, the management team must closely monitor the situation, to maintain each level of a manual system, there is a significant amount of documentation and administration to be done (Tavares, Da Silva, and De Souza, 2019). As any other telecommunications firm, Telstra Corporation has several risks that it needs to address before they develop into severe issues for the company. Failure to take the necessary measures before performing such an operation could have profound implications.
The capacity of Telstra Corp., just like any other business entity, to achieve its goals is threatened if it fails to foresee, detect, and mitigate any potential hazard. As part of its long-term strategy to detect and respond to possible threats it is exposed to, its risk assessment efforts should not be an afterthought (Barafort, Mesquida, and Mas, 2019). Risks become “problems” when they occur and result in dire consequences, and a risk Telstra cannot afford to take. Diverse businesses will interpret the term “risk management” in different ways. Major organizations may have to conduct significant risk analyses as part of their portfolio management plans. Rigorous analysis in finding, classifying, analyzing, and formulating methods for dealing with potential hazards (Yang, Ishtiaq and Anwar, 2018). Telstra Corp. is no exception for mitigating potential hazards it faces.
Telstra Corporation has established an Audit and Risk Committee, which David Hitchcock oversees. The team’s primary responsibility is to guarantee that the company complies with the laws and regulations that govern it in Australia—as a result, charging the team with the duty and responsibility of developing the risk management program guidelines. The aim is to ensure that the least amount of loss happens in the event of any uncertainty at Telstra. Therefore, Hitchcock and his team determine how any risks have resulted in losses in terms of property, liability, income, and personnel exposure and treat those losses accordingly. They are assigned the responsibility of ensuring that the actions that take place run smoothly and with the least amount of intervention as is reasonably practicable.
The team has the duty of maintaining necessary appropriate accounting and financial reporting principles and policies, risk management processes, and internal controls and procedures. Designing all this ensures compliance with accounting standards and the applicable laws and regulations (Ghasemi et al. 2018). Therefore, the team designs and implements an appropriate and effective risk management framework while ensuring an influential risk culture within the organization. The team accesses selected risks and reports to Telstra’s management team on the emerging and escalating sources of risks and the risk management plan it has put in place to deal with the risks. Upon reviewing the report, the management implements the recommendations issued to mitigate the occurrence of the risk.
It is the team’s responsibility to ensure that it monitors and evaluates the level of compliance and governance at Telstra. Lack of compliance would cause dire consequences to the organization, leading to avoidable losses. Failure to comply with applicable laws could lead to lawsuits that would destroy the reputation and image of the organization. Proper monitoring, therefore, ensure that the committee has a mechanism for proper risk identification (Zaveckaite and Ulbinaite 2018). It entails having a platform throw which whistleblowers can air their concerns regarding non-compliance and still protect without infringing any of their rights.
Risk identification
Risk Identification refers to the processes that organizations and industries employ to determine threats and damages that can be detrimental and interrupt corporate operations derailing them from achieving their long-term potential. In order to have a well-established risk management system in an organization, risk identification is critical as it gives the management an overview of threats and prepares themselves with necessary precautions. Risk identification is an ongoing process throughout the life cycle of an organization (Tserng et al., 2021). Telecommunication corporations such as Telstra rely heavily on the internet and much other sophisticated software that can pose high cyber security threats. Lawsuits, theft, financial liquidity, terrorist attacks, and natural catastrophic occurrences are common risks affecting all departments.
Tools and procedures that management can use to identify risks include. Project-related documentation, such as lessons learned articles and organizational processes, is reviewed to detect potential hazards. Information-gathering techniques include brainstorming, interviewing, the Delphi methodology, root cause analysis, and swot analysis. Like many other companies, Telstra has conducted a SWOT analysis to see where it could be vulnerable. It recognizes its power over a sizable portion of the market and knows its vulnerabilities, opportunities, and dangers. Figure 2 shows a summary of SWOT analysis:
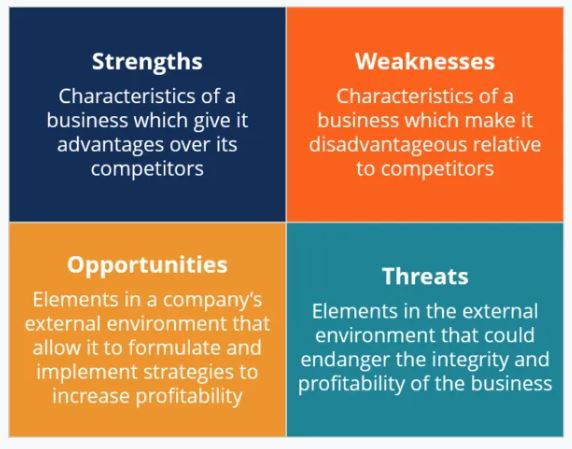
It is the mandate of the risk management committee to come up with approaches and strategies for risk identification. Brainstorming is one of the techniques used to identify a potential risk at Telstra Corp. The risk management committee conducts meetings with all employees to discuss potential risks experienced in different departments and then narrows down possible ways to counter the problems. At this point, one of the major risks identified included cyber security, which affected Telstra directly after one of its subsidiary data companies was hacked. Due to its vast nature, department managers may not be in a better position to identify risks in an institution and hence rely on the feedback of departmental employees. The Nominal Group Technique (NGT) is necessary as it gives in-depth risky situations in the company (Althonayan and Andronache., 2018). The NGT method provides a more efficient risk identification as it gives comprehensive and honest views on the challenges they face in their workstations.
Big corporations such as Telstra are not individual but rather consist of several shareholders. Shareholders such as Gabelli Funds LLC and Yousif Capital Management LLC monitor the operation of the business to ascertain any treats from an outside perspective. Therefore, conducting shareholder interviews frequently helps the Corporation identify areas that need reinforcement. Due to the considerable investments in the Corporation, shareholders critically analyze areas that may result in the loss of their investments.
During the planning of the business activities, a pessimistic way of thinking is critical. Even though owners and shareholders need to be optimistic about the business, they need to prepare the risk management team critically to prepare for the worst while expecting the best. It will help the committee locate the necessary resources to counter the risks in case they occur. It is vital to plan for the worst while targeting to achieve the best since the company will not incur losses if the risk does not occur. Conducting a previous record examination may help the team identify what they dealt with before. The root cause analysis helps identify the risk simultaneously, giving room to change an approach on how to deal with it since the previous did not work.
Risk analysis and evaluation
Doing a risk analysis entails locating and evaluating any elements that may pose a threat to the profitable operation of a certain commercial firm. It outlines the complete procedure used to identify the dangers and risk factors that might impact the business and its operations. As a result, the procedure provides the organization with an opportunity to investigate the possible threats that are confronting the company and, as a result, to devise an appropriate system that will assist in addressing the issue.
Telstra Corporation is exposed to several possible dangers, some of which include, but are not limited to, the possibility of the loss or theft of personal customer data, fraud, and business interruptions caused by viruses and malware. If the company does not adequately manage these risks promptly, it might face significant issues in finances, reputation, or even the law, which could have potentially damaging implications. Because of this, David Hitchcock and the rest of his team need to concentrate on each risk that has been identified and conduct an in-depth analysis of it to determine the potential negative effects that it poses to the organization as well as the various ways in which the company can reduce the risk.
During the process of analyzing the risk, the team must be able to determine who may be impacted by the risk that has been discovered. This is clearly illustrated in the figure 3 shown below;
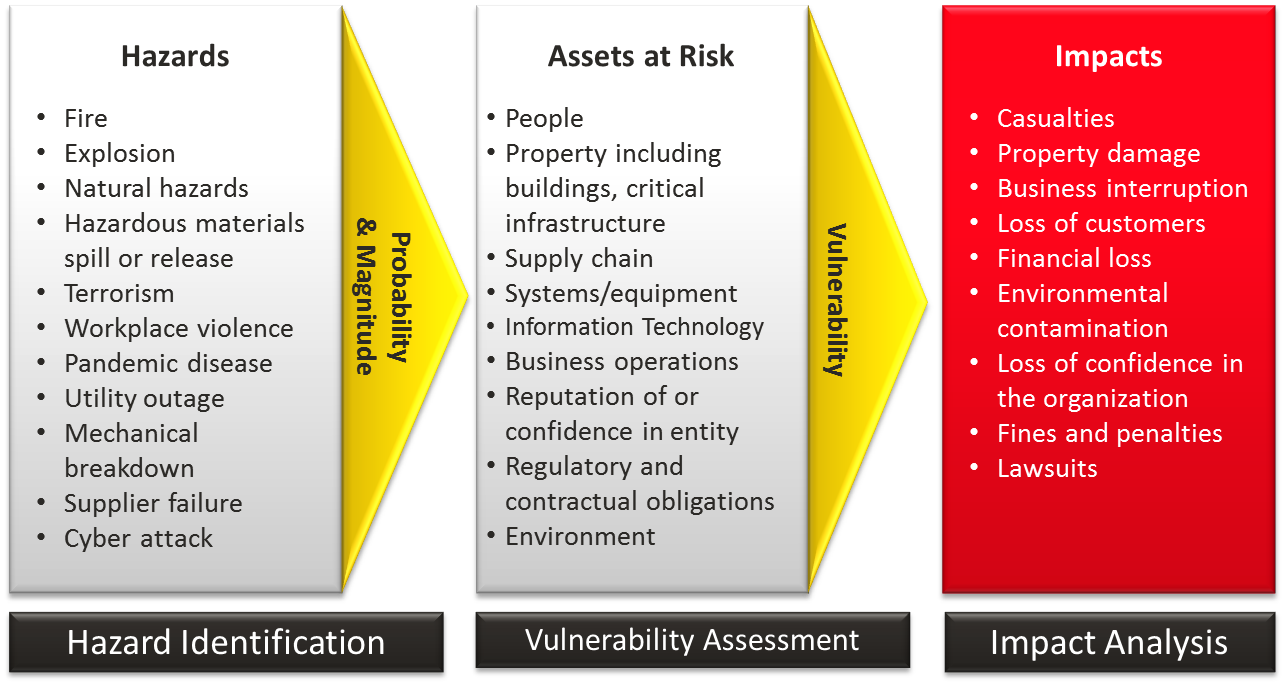
Every shareholder is at risk of becoming a casualty, even if the company’s image is not tarnished because the company’s reputation is in jeopardy (Hillson, 2019). It might be the company’s owners, the employees, the customers, or even the company’s area. Because of this, no information on any risk must be disregarded because the company is in danger from every risk (Burdon and Mackie, 2020). Consequently, Telstra has built a framework to preserve and protect the rights of all whistleblowers, both inside and outside of the business.
Risk treatments
The term “risk treatment” refers to the methods companies put into practice to eliminate or significantly cut down on the likelihood that hazards may materialize. There are two distinct categories of danger: those that call for immediate action and those that can be dealt with later. Nevertheless, to decide how to deal with the danger, it is essential to have a strategy for doing the same thing (Xu, 2020). The plan needs to provide an outline of the processes that Telstra will use in the process of treating the risk, as well as the personnel that the organization will use to treat the risk, the financial cost that Telstra will be involved in, as well as the benefits that the treatment will have on the company and other stakeholders.
Cyber-attacks and Ransomware are the most common destroying risks a company like Telstra might face. All of its activities revolve around the internet, and online activities, including sensitive data and information backup, place it at risk of cyber-attack. A recent instance is what happened in 2021 when hackers breached and gained access to Schepisi Communication system that is a dealer to Telstra corporation supplying it with sim cards and cloud storage. The risk needs to be acted upon with an extreme agency, or it may lead to the closure of the entire company and its affiliates. Therefore, this specific risk can be addressed and treated by patching outdated software both in all operating systems and all the applications used in the company (Hillson and Simon, 2020). It can be achieved by turning on the system updates in all the devices across all the departments and ensuring all plugins, such as flash discs, are updated.
The use of anti-virus protection and firewall helps protect the organization from malicious viruses. The two-factor verification method is very critical in major corporations such as Telstra, and it guarantees the protection of data as it makes it hard for hackers to breach. Backing up data regularly helps mitigate potential risks that could result in the loss of a company’s most important information.
They did this by avoiding business development strategies that have the potential to put the company in jeopardy. For instance, they steered clear of partnerships with shareholders or suppliers who might be vulnerable to attacks and, as a result, pose risks to the organization. It allowed them to avoid the risk that Telstra would ultimately realize. When it was taken to court by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission in 2020, Telstra discovered that it had violated a legal provision and was in the wrong (ACCC) (Howell and Potgieter., 2020). Telstra engaged in unethical marketing practices that violated the legislation protecting consumers from promoting its products. Telstra may have avoided the possibility of paying a penalty of $50 million.
In some cases, risks cannot be avoided entirely, but strategies to reduce their effects can be used. It can be achieved through training staff or different specialties within the organization so that in case of any resignation, the company will not be affected suddenly. Risk reduction treatment can help lower the impact a risk would have caused by employing approaches and guide in case of an emergency (Zaveckaite and Ulbinaite 2018). Ensuring the business helps transfer risks to other third parties, reducing the weight of loss solely to an organization. Alternatively, a business entity may accept the risks if they are beyond control; this could be risks such as natural disasters such as hurricanes.
Risk management integration
An old-school risk management strategy entails identifying various hazards and delegating them to various risk specialists, each with their own set of tools. A siloed risk management strategy leads to a limited view of risk reduction, which does not add value to businesses. Organizations can better align and maximize the benefits of this approach by taking into account all risks and procedures in use with an integrated risk management strategy (IRM) (Smith and Merritt, 2020). Businesses can now shift the focus of risk management away from assessing an organization’s exposure to threats by combining various risk management activities into an operating risk framework as shown in figure 4 below:
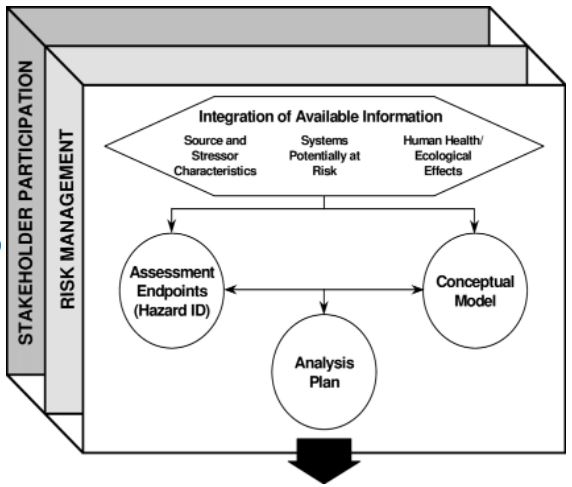
As a result, it is critical to approach risk management holistically to understand how different hazards interact. So, after examining how these risks and associated changes would affect the organization’s overall structure, expert teams can develop risk mitigation strategies (Deshmukh, Mukerjee, and Prasad, 2020). Incorporate risk management practices into the daily operations to improve chances of success. A firm must implement an Integrated Risk Management strategy to succeed in today’s global marketplace.
Users and application systems may be provided with dependable, verifiable, and consistent data when a company implements integrated risk management. Businesses can utilize dependable and safe data, which enables them to satisfy compliance criteria as a consequence of the integration of the data of many specialists. Consequently, the corporation is now able to develop and manage new organizational structures and inter-organizational relationships, which may be the outcome of mergers and acquisitions. Businesses may minimize service or product delivery delays caused by erroneous data by establishing, implementing, and measuring data quality plans and metrics with integrated risk management, which can do all of these things (Pham et al., 2021). Integrated risk management can avoid work stoppages, catastrophic disasters, and other risks to the organization’s ability to function.
A significant amount of support is available for evaluating which approach, goals, and level of risk appetite are ideal for managing the already identified risks. When leadership teams better understand the impact risks have on the strategic and operational goals, they can make more informed decisions (Xu, 2020). It is possible to keep an eye on several potential dangers simultaneously. As a direct consequence of this, risk assessment at the organizational level and the interrelationships between the various types of risk become clearer. IRM may be able to more properly assess and evaluate risk mitigation management solutions when it incorporates occurrences beyond the scope of the risks being examined (Witzleb, 2017). Identification, analysis, and assessment of potential dangers may be carried out more quickly with the help of IRM. Management teams can better use the resources they have access to thanks to effective risk management, enabling them to make more informed allocation choices.
Findings and recommendations
According to the findings of this study, Telstra still has a considerable amount of potential to enhance both the quality of its products and the efficiency of its business processes. Because of its affiliates and dealers, the company is more vulnerable to cyberattacks, which reduces the efficacy of the company’s attempts to defend itself against such dangers. A breach in the organization’s security systems might lead to confidential information about its customers being exposed, which would violate those customers’ right to privacy. An issue with a dealer’s performance might affect a company’s reputation, as demonstrated by the hack that was carried out against Schepisi Communication in Melbourne.
In addition, the study of the paper investigates the possibility that the sales and marketing divisions of the corporation are participating in unethical business activities to promote and sell the company’s products. The consumer protection provision is disregarded in the business practices used for marketing. Even though the company’s objective is to achieve the highest possible level of profitability, the strategy that it employs inevitably puts it in conflict with the law. As a consequence, the business is forced to pay significant financial penalties. It is imperative that a plan to promote the utilization of more sophisticated firewall services be put into effect as soon as possible. It is feasible to carry out internal and external audits and online account assessments to keep an eye on potential risks in the workplace. It is made possible as a result of the threats posed by cyber-attacks. It gives management the ability to assess any security flaws in the system that may have been caused by related information from an individual working for the firm.
To ensure that all information is inaccessible in a system breach, the Telstra corporation must keep its lead in multiple locations that are not connected. The use of unimaginable solid passwords and two-factor verification in data protection needs to be considered (Rahman and Adnan 2020). Telstra’s cloud storage needs to have secure access that can only be accessed by the company and not its dealers and affiliates.
As a final proposal, Telstra needs to train all of its workers, particularly those involved in market research, sales, and marketing, to comply with legal standards for marketing and advertising to avoid raising red flags with customers. The loss of even a single customer can have a significant impact because customers tend to stick together. Failure to adhere to a few fundamental rules in marketing might decrease revenue for a business.
References
Althonayan, A. and Andronache, A., 2018, September. Shifting from information security towards a cybersecurity paradigm. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Information Management and Engineering (pp. 68-79).
Barafort, B., Mesquida, A.L. and Mas, A., 2019. ISO 31000‐based integrated risk management process assessment model for IT organizations. Journal of Software: Evolution and Process, 31(1), p.e1984.
Burdon, M. and Mackie, T., 2020. Australia’s Consumer Data Right and the Uncertain Role of Information Privacy Law. International Data Privacy Law (2020), 10(3), pp.222-235.
Deshmukh, G.K., Mukerjee, H.S. and Prasad, U.D., 2020. Risk management in global CRM IT projects. Business Perspectives and Research, 8(2), pp.156-172.
Ghasemi, F. et al. 2018 ‘Project portfolio risk identification and analysis, considering project risk interactions and using Bayesian networks’, Sustainability, 10(5), pp. 1609-1631.
Hillson, D., 2019. Capturing Upside Risk: Finding and managing opportunities in projects. Auerbach Publications.
Hillson, D. and Simon, P., 2020. Practical project risk management: The ATOM methodology. Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
Howell, B.E. and Potgieter, P.H., 2020. Politics, policy and fixed-line telecommunications provision: Insights from Australia. Telecommunications Policy, 44(7), p.101999.
Pham, D.H., Ly, D.H., Tran, N.K., Ahn, Y.H. and Jang, H., 2021. Developing a Risk Management Process for General Contractors in the Bidding Stage for Design–Build Projects in Vietnam. Buildings, 11(11), p.542.
Smith, P.G. and Merritt, G.M., 2020. Proactive risk management. productivity press.
Rahman, M.S. and Adnan, T.M. 2020 ‘Risk management and risk management performance measurement in the construction projects of Finland’, Journal of Project Management, 5(1), pp. 167-178.
Tserng, H.P., Cho, I.C., Chen, C.H. and Liu, Y.F., 2021. Developing a Risk Management Process for Infrastructure Projects Using IDEF0. Sustainability, 13(12), p.6958.
Witzleb, N., 2017. ‘Personal Information’under the Privacy Act 1988 (Cth)-Privacy Commissioner v Telstra Corporation Ltd [2017] FCAFC 4.
Xu, J., 2020. Essential Topics of Managing Information Systems.
Yang, S., Ishtiaq, M. and Anwar, M. 2018 ‘Enterprise risk management practices and firm performance, the mediating role of competitive advantage and the moderating role of financial literacy’, Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 11(3), pp. 35-51.
Zaveckaite, A. and Ulbinaite, A. 2018 ‘Assessment criteria of project risk management in language translation service companies’, Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 24(4), pp. 1323-1343.