Executive Summary
The United States has faced a persistent nursing shortage that has intensified in recent years due to factors such as workforce aging, limited educational capacity, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although past efforts—including increased funding, higher salaries, and expanded nursing education—temporarily alleviated the problem, the demand for nurses continues to outpace supply. This shortage threatens patient care quality and forces hospitals to rely on costly temporary and foreign nurses. In response, legislative initiatives like the Stop Nurse Shortages Act and new organizational strategies are being developed. The current strategic plan aims to address this staffing crisis through enhanced funding, improved compensation, and expanded training opportunities, supported by private investors committed to ensuring sustainable workforce growth.
Goals, Objectives, and Strategies
Setting
It is essential to note that to conduct a strategic plan, an organization needs to define goals and strategies. Thus, the primary purpose is to improve the number of nurses delivering quality patient assistance. Similarly, enhancing their working essentials is also a goal, as it helps improve nurses’ satisfaction levels (Marć et al., 2019). Accordingly, by improving the working atmosphere in the organization, it is possible to decrease the number of releases and staff turnover.
Moreover, the next objective is to promote further training of nurses. To achieve this goal, it is essential to involve them in scholarly programs and provide opportunities for career growth. The primary task is to improve the recruitment of nurses over the next two years. During this period, it is required to attract 32 percent more staff than last year.
Another goal is to reduce nurse decay by 30 percent over the next year (Marć et al., 2019). Furthermore, the organization must offer three areas of training for nurses to choose from and revise the courses yearly. The next challenge is to work with additional recruitment companies to attract more professional staff to the organization.
Achieving
To fulfill the goals and objectives, the main method is to cooperate with schools that train nurses. This is required to attract the best graduates to work in the organization and to create experienced and educated nurses. It is also necessary to conduct surveys among nurses and analyze their feedback on working prerequisites in the community (Marć et al., 2019). Such a strategy will enhance their job satisfaction and authorize managers to consider all the needs of nurses. Furthermore, selecting a training fund will help nurses to continually enhance their understanding and facilitate their stay in the organization.
Evaluating Outcomes
Nevertheless, monitoring, evaluating, and recognizing success in achieving objectives, strategies, and goals is essential. For example, the number of nurses can be increased by calculating the number of new nurses engaged over a specific period (Marć et al., 2019). Progress can be tracked through a system of monthly messages from the HR department.
In addition, success in enhancing the conditions of nurses can be measured by lowering the number of nurses retiring. To monitor and evaluate progress, it is critical to have a close connection with the HR department. However, paying attention to the explanations of the nurses who desire to leave is important. This will allow the reasons for their departure to be apprehended and modifications to be made to retain attendants.
Furthermore, increasing nurse participation in educational programs can be a measure of success in advancing nurse training and instruction. This can be done by surveying nurses about their professional skills and knowledge. Another way to achieve recruitment goals is to create a comprehensive plan and implement it gradually (Marć et al., 2019). To gauge recruitment, track recruitment sources, and determine the effectiveness of each method.
Stakeholders’ Roles
Moreover, stakeholders have specific needs when creating a strategic plan, so the goals, dreams, and plans should align with their needs. Therefore, the plan should eliminate the organization’s medical staff shortage and improve their conditions. Respond promptly to patients’ conditions and enhance their satisfaction with the organization’s benefits (Marć et al., 2019).
Another stakeholder need is to improve patient volume, so they expect efficient hiring strategies and fast reversal times. In addition, stakeholders require clear coordination of actions and implementation within the organization, so they need to be provided with a system for reporting and verifying success. Furthermore, nurse training is essential for stakeholders because it enables them to establish mutually beneficial relationships.
Proposed Core Team of Change
Stakeholders
Chief Nursing Officer
It is essential to note that internal stakeholders are crucial in implementing the strategic plan to address the nursing shortage within the organization. One such stakeholder is the chief nursing officer (CNO). The CNO is in control of the nursing division and can directly impact the quality and satisfaction of nurses, as they understand the needs and expectations of nurses (Marć et al., 2019).
Director of Human Resources
The director of human resources is also an essential stakeholder in recruitment. The recruiter’s experience is necessary for shaping recruitment processes and effectively addressing nurse retention issues within the community. Moreover, the nursing department leader is another stakeholder, as they have direct experience with nurses and can quickly identify urgent issues (Marć et al., 2019). This enables them to settle conflicts and manage the staff so that nurses do not need to depart.
Partner Organizations
It is also worth emphasizing external stakeholders, namely, nursing schools, with whom the organization will partner. This is important because they are curious about creating career opportunities for their graduates and employees. Moreover, healthcare and community companies are external stakeholders interested in the organization’s ability to provide quality patient care (Marć et al., 2019). Accordingly, they are willing to work together to facilitate the nursing shortage by providing a budget or helping to implement modifications and creations.
Collaboration with Stakeholders
Workshops
Stakeholders will be actively involved in the strategic planning process through various methods. For instance, collaborative workshops can be held where all stakeholders can debate ideas and solutions to the nurse shortage. The benefit of this method is that it allows organizations to select the best exercises and ideas to implement (Marć et al., 2019). Moreover, personal meetings are a way to objectively assess the challenges that exist in the community. Each stakeholder can individually offer help in solving specific problems.
Communication
The following procedures will be operated to promote cooperation and contact with stakeholders. They need to be provided with constant updates to guarantee that the stakeholders have up-to-date information. They should also communicate with the organization’s representatives through phone calls, emails, or unique platforms. In such cases, they can ask questions and provide guidance to reduce the shortage of nurses in the community (Marć et al., 2019). It is also crucial to create platforms for co-doing, where each player can see the progress together.
Motivation
Stakeholders need to be inspired and involved in implementing the strategic objective. Their contribution should be publicly recognized and respected. Moreover, they must be provided with regular information on the organization’s efforts to address the nursing force issue. This way, stakeholders will feel needed and critical in achieving a shared goal (Wadsworth et al., 2016).
Another way to involve and encourage them is to formulate a common goal and objectives. As a result, this will allow them to work together and harmonize their actions. In this way, stakeholders will share a common vision for reducing the nursing shortage in the community.
Generally, a strong team comprising both internal and external parties is key to successfully implementing an organization’s strategic plan (Wadsworth et al., 2016). Therefore, paying attention to each other and communicating separately in case of issues is essential. As a result, this will help maintain the trust and reliance of stakeholders and enhance overall collaboration.
Budgeting and Timeline Tools
Expenditures
Recruitment, Training, and Retention
Crucially, a strategic plan to reduce the nursing shortage requires a financial analysis to evaluate its success. The budget encompasses various categories, including recruitment, training, retention, and stakeholder collaboration. The financial indicator encompasses recruitment efforts, including budgeting for marketing and advertising (Wadsworth et al., 2016). In addition, staff training incurs additional financial costs for developing and implementing programs, as well as creating training resources.
Moreover, it is necessary to finance retention initiatives to ensure that nurses remain with organizations and do not change jobs, thereby reducing the staff shortage. Accordingly, providing them with additional benefits and allocating funds to enhance their workplace is necessary. This will help motivate nurses to work for the organization and to involve their friends (Lown et al., 2019).
Stakeholders
Another factor that has a financial impact is the involvement of stakeholders in implementing the strategic plan. Therefore, ongoing expenditures on partnership development and dissemination of information about the organization’s problems are necessary to attract new sponsors. It is essential to note that the financial impact of the strategic plan will also depend on the overall nurse shortage, the regional situation, and the ability to offer favorable working conditions to qualified nurses.
Table 1: Financial Impact
Timeline
The Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) diagram demonstrates the timeframe required for change. The primary advantage of the PERT tool is that it accommodates uncertainties and disagreements. Accordingly, the tool is effective because it can make various forecasts. For example, one can define indicators for optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic time estimates (Lown et al., 2019). Accordingly, implementing the strategic plan is less likely to encounter barriers.
Table 2: Timeline of the Strategic Plan
The total project duration is estimated to be between 118 and 189 days, encompassing optimistic, most probable, and pessimistic time estimates. The PERT chart is a method for identifying the likelihood of unplanned situations and finding solutions to them. It is also designed to provide flexibility and planning for unforeseen circumstances. Thus, it enables the team to effectively manage potential delays or deviations.
As a result, project deadlines will not be shifted, and people involved in the implementation will be able to use resources efficiently. Hence, another advantage of this method is that it allows for consideration of variance. This is particularly necessary in today’s rapidly changing environment, especially when financial resources and stakeholders are involved.
Balanced Scorecard
Components
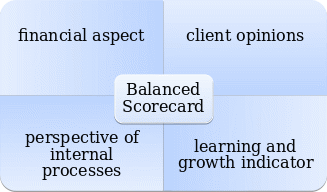
A balanced scorecard to address the nursing shortage has four core dimensions. First is the financial component, which comprises the cost of training and hiring. Second, the balanced scorecard integrates patients’ opinions, providing statistics based on their responses and assessing customer satisfaction (Gilbert, 2023). The third indicator is the perspective of internal processes, which includes the incidence of nurse resignations and the number of openings. The fourth component is the learning and growing dimension, which comprises staff members’ development and occupational advancement.
Performance Indicators
However, there is no balanced scorecard to measure and evaluate the impact of changes while implementing the strategic plan to decrease the nursing deficit. Therefore, a system of indicators enables the connection of goals with performance indicators (KPIs) (Gilbert, 2023). Thus, it enables the estimation of progress and the implementation of improvements promptly. By setting specific financial goals, you can improve training costs and, from an internal process perspective, reduce staff attrition.
For this reason, collecting and measuring data from multiple sources, such as staff surveys, patient surveys, and nurse turnover trends, is critical. This way, monitoring and reports will track the performance and constantly refine the balanced scorecard. Thus, the balanced scorecard will fairly measure the four core performance indicators to identify their effectiveness (Gilbert, 2023).
Accordingly, this will enable us to determine the priority area for which the nurses should be enrolled. Additionally, the proposed system provides a method for reviewing the changes already made. For instance, an organization’s goal to decrease the nursing shortage may evolve and must be constantly adjusted to the balanced scorecard (Gilbert, 2023). Hence, it allows one to evaluate positive and negative variations and quickly introduce the staffing concept.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
It is essential to remember that assessing the rationality of the project requires evaluating the project’s costs and benefits. To achieve this goal, the community can conduct a cost-benefit analysis. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the investments made to address the nursing shortage. Additionally, funding for training and workplace modifications should be contained in the costs (Gilbert, 2023). Then, the costs are compared with possible advantages, such as reduced nurse turnover, improved qualified staff, and patient dignity.
Accordingly, using a balanced scorecard enables the assessment of the effectiveness of each dimension of initiatives. Therefore, it should be used to estimate the future result that can be obtained (Gilbert, 2023). Additionally, it is appropriate to use this approach since it allows for the modification or removal of initiatives if they are not working. This way, the most favorable channels for attracting and retaining nurses can be identified and resourced.
The scorecard will indicate positive tendencies if the projected outcome exceeds estimates and the benefits outweigh the expenses (Gilbert, 2023). Therefore, it is critical for a strategic plan to improve the number of nurses in an agency. Finally, with the help of a balanced scorecard, it is now possible to adjust costs, thereby enhancing the chances of project implementation.
References
Gilbert, J. H. (2023). Investment in social capital to mitigate nursing shortages post-pandemic. Nurse Leader, 21(1), 69-74. Web.
Lown, B. A., Shin, A., & Jones, R. N. (2019). Can organizational leaders sustain compassionate, patient-centered care and mitigate burnout? Journal of Healthcare Management, 64(6), 398-412. Web.
Marć, M., Bartosiewicz, A., Burzyńska, J., Chmiel, Z., & Januszewicz, P. (2019). A nursing shortage–a prospect of global and local policies. International Nursing Review, 66(1), 9-16. Web.
Wadsworth, B., Felton, F., & Linus, R. (2016). SOARing into strategic planning. Nursing Administration Quarterly, 40(4), 299-306. Web.