Introduction
Alcoholism is one of the most widespread and dangerous social problems in the United States and around the world. This issue is characterized by excessive drinking and loss of control. Alcohol affects people in different ways, in some cases, a person can stop drinking, but sometimes specialists’ help is required to abandon this habit. According to experts, “the lifetime prevalence of alcohol abuse in the United States is estimated to be around 18%” (Mehta, 2016, para. 1). It also affects physical and emotional health, social status, work, and relationships with family.
SBIRT description
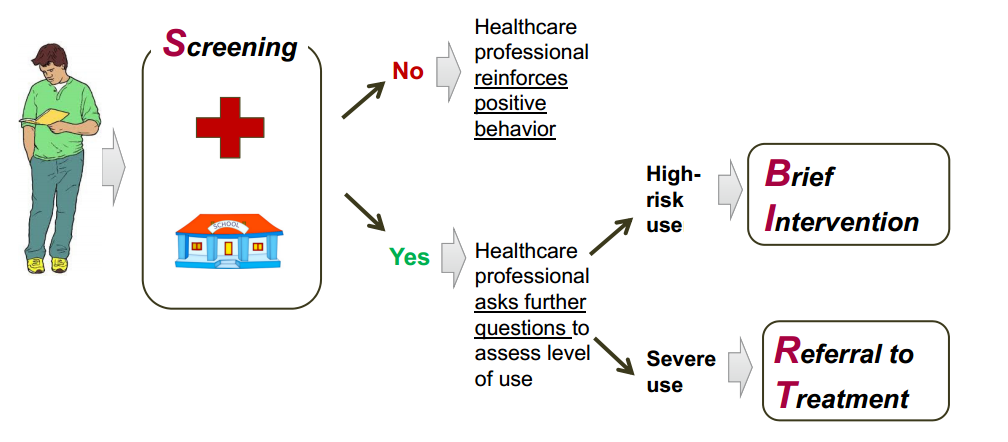
In recent years, the Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment method, or “SBIRT,” has become an effective tool for screening and solving behavioral health problems, including alcohol addiction (McKnight, 2016). The primary goal of SBIRT is to identify people who are at moderate or high risk for psychosocial or health care problems. SBIRT provides an identification of levels of risk, of patients who would benefit from brief advice and those who would benefit from higher levels of care (McKnight, 2016). It uses specific steps: pre-screening, full screening for those with a positive pre-screen, brief intervention for those scoring over the cutoff point, brief treatment, and referral to treatment.
Problem Description
Alcohol addiction is a chronic neurological disease which damages all the body’s organs and the person’s nervous system. The huge losses that alcohol abuse has caused to individuals, families, and communities in the United States have led to a severe public health crisis (Mehta, 2016). Alcoholism increases the risk of a large number of diseases, especially oncological types of diseases. Drinking weakens the human immune system, provokes various pathologies of the brain, and leads to liver destruction. Everyone knows that pregnant women are forbidden to consume alcohol since the probability of having a birth with pathology growths significantly (Mehta, 2016). The regular drinking leads to premature old age, disability, and a decrease in life expectancy. It is an extremely crucial problem of modern society, as it directly affects the future of citizens.
Community Resources
There are some community resources for people who have an alcohol problem or an increased potential for acquiring this problem. For example, Maryland SBIRT provides highly qualified support. It is a nationwide community that helps improve healthcare and encourages people to discuss alcohol and drug use during routine medical visits. This program aims to reduce drug and alcohol addiction, optimize the health care system in Maryland, and improve the quality of public health. Another useful community resource is Columbia SBIRT. Its goal is the quick and effective identification of patients for further evaluation or treatment for alcoholism and drug addiction.
Conclusions
To sum up, SBIRT (Screening, Brief Intervention, Referral to Treatment) is a comprehensive approach of the healthcare system to provide early intervention and treatment services for people with alcohol or drug addiction. Unlike traditional treatment, in which health patients have to get therapy, SBIRT is non-prescriptive. This conception does not condemn certain health behaviors. It ensures that patients are aware of their behavior, prevents the development of addiction and motivates to change.
The video “SBIRT in Primary Care: At-Risk Alcohol Use” (2015) is about Mr. Walker, who came in for his annual check-up. He completed the health center’s yearly alcohol screen questionnaire and screened positive on his single question alcohol screen; thus, Mr. Walker was asked to complete the AUDIT. His nurse reviewed the results with him and engaged Mr. Walker on goals to change his alcohol use using the Brief Negotiated Interview.
References
McKnight, B. C. (2016). The SBIRT Method for Alcohol Misuse Screening and Treatment.
Mehta, A. J. (2016). Alcoholism and critical illness: A review. World Journal of Critical Care Medicine, 5(1), 27-35. doi:10.5492/wjccm.v5.i1.27
SBIRTonline. (2015). SBIRT in Primary Care: At-Risk Alcohol Use [Video file].