Introduction
Starbucks is a worldwide famous chain of coffeehouses and roaster reserves. The business was established in Seattle in 1971 and currently owns over 16,800 stores in North America and more than 17,000 locations over the world (Yahoo.Finance, n.d.). Starbucks serves coffee, tea, roasted beans, and different food products, which is attractive to millions of customers from various countries. It is worth admitting that this entity is a corporation (Yahoo.Finance, n.d.). This type of business implies that a legal entity is distinct from its owners, meaning that Starbucks has almost the same rights and responsibilities as ordinary people. Thus, it is reasonable to look at how the corporation handles its financial well-being.
Discussion
To begin with, one should explain why Starbucks needs funding. The rationale behind this statement is that financial resources are typically required to promote the further growth of the business. Furthermore, additional funding should be generated when a company wants to invest more in the research and development field to find innovative solutions or introduce new products to the market. Since these decisions can be made by Starbucks, the given business entity should consider what funding sources can be applied.
It is rational to comment on what sources of funding are available, and Starbucks can rely on three options. Firstly, the corporation can implement self-funding approaches, meaning that the business entity can use some of its generated revenues to achieve the goals above. Secondly, debt funding can also be used, and this approach denotes that a company borrows money and promises to return them in the future. Thirdly, Starbucks can rely on equity capital to grow and develop. This option implies that the corporation allows investors to buy its shares.
Each source offers certain requirements and risks, and Starbucks should consider them. As for self-funding, the corporation needs a sufficient amount of revenue so that it can use some of them to foster growth and development. That is why a risk refers to the fact that such a funding approach can result in significant losses for the company. Debt funding can be used if Starbucks manages to find a lender that will provide a sufficient amount of financial resources (Yacus et al., 2019). However, a risk is associated with the fact that it will be necessary to pay an interest rate, which can become challenging. In turn, equity funding implies that the corporation should issue its shares, and a specific number of investors are ready to purchase them. A negative aspect relates to the fact that shareholders own a part of the corporation, meaning that Starbucks can lose some control over its entity (Yacus et al., 2019). This information demonstrates that each funding source implies advantages and disadvantages for the corporation.
According to the findings above, it is possible to claim that self-funding is currently the most appropriate for Starbucks. The rationale behind this statement is that the corporation’s revenues kept growing for the last five years if 2020, with its COVID-19 crisis, is excluded from the statistics (Macrotrends, 2022). Consequently, Starbucks generates sufficient profits, and it can use them to achieve specific goals. Since the other two sources are riskier, they are less preferred. However, the corporation can still rely on them, and the decent financial performance described above demonstrates how Starbucks can address the existing risks.
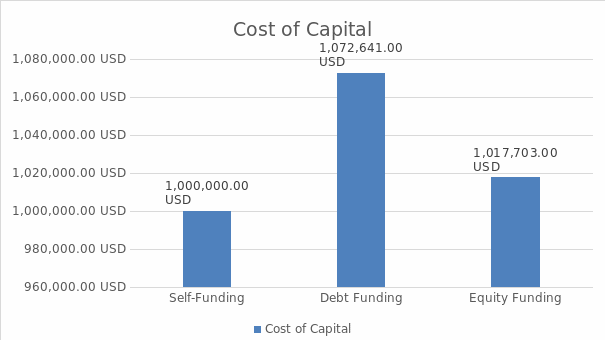
If it is necessary to estimate the cost of capital, the exact amount depends on how much money Starbucks needs, the annual percentage rate (APR), and the period. If the corporation needs $10 million, it is possible to make estimations. The self-funding approach is appropriate in the long run because the corporation does not need to pay additional interest for using the money. Thus, the long-term cost of capital equals $1 million because APR is 0%.
However, the state of affairs is different when debt and equity financing are considered in the short run. On the one hand, the APR for debt financing is 4.6% (Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, 2022). Consequently, the cost of capital for the 3-year term is approximately $1,072,000. On the other hand, if the corporation needs to generate $1 million through equity funding, it should sell 13,115 shares because a single share price is $76.25 (CNBC, 2022). In a 3-year term, Starbucks will have to pay $17,703 of dividends since the corporation mentioned that its dividends were $0.45 per share (Starbucks, 2021). Thus, the cost of capital is estimated at $1,017,703. Graph 1 below demonstrates the comparison of these values for the three funding sources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is possible to rely on the available data to make a profit-and-loss statement for a 3-year period. According to Macrotrends (2022), the corporation’s gross profit was $15,321 million in 2017, $16,788 million in 2018, $17,981 million in 2019, $15,823 million in 2020, and $20,320 million in 2021, future forecast is possible. Thus, it is expected that the gross profits will keep rising, accounting for $21,000 million in 2022, $23,000 million in 2023, and $24,000 million in 2024. Furthermore, the corporation’s direct costs can be associated with the store operating expenses that are described in Starbucks’s annual report, stating that these costs are $11,930 million (Starbuck, 2021). Thus, all this information demonstrates that Starbucks can impress with good financial health.
References
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. (2022). Consumer credit – G.19. Federal Reserve. Web.
CNBC. (2022). Starbucks Corp. Web.
Macrotrends. (2022). Starbucks financial statements 2009-2022 / SBUX. Web.
Starbucks. (2021). Fiscal 2021 annual report [PDF document]. Web.
Yacus, A. M., Esposito, S. E., & Yang, Y. (2019). The influence of funding approaches, growth expectations, and industry gender distribution on high‐growth women entrepreneurs. Journal of Small Business Management, 57(1), 59-80.
Yahoo.Finance. (n.d.). Starbucks Corporation (SBUX). Web.