Coca-Cola: A SWOT Analysis
Assessing the performance of Coca-Cola, as one of the largest and recognized global corporations, through a comprehensive analysis of its business characteristics can help identify real growth prospects and determine constraints and limitations that affect the company’s operations. One of the mechanisms for such an evaluation is a SWOT analysis that, according to Phadermrod et al. (2017), is “a commonly used tool for strategic planning” and implying “Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats” (p. 194). Due to the global activities of the corporation and the active increase in its production points, the Coca-Cola business can be viewed in an international context. However, focusing on a specific region, particularly the Gulf countries, can help identify specific trends and factors that determine the nuances of a company’s business. Applying the SWOT methodology is a practical solution to evaluate the different perspectives of Coca-Cola’s business and draw objective conclusions based on this data.
The first component of the analysis includes the strengths of the business in question. Coca-Cola has a number of advantages over other brands that allow the corporation to promote its business successfully. As Abbasi (2017) argues, the Coca-Cola brand soft drinks are the world’s best-selling beverages and are offered to consumers in more than 200 states. Such marketing success is due to a long presence in the market, a stable client base that is constantly expanding, as well as competent marketing decisions. In addition, product diversity is a significant strength of Coca-Cola’s business. A variety of non-alcoholic drinks are offered, which helps attract new customers and increase brand loyalty. Walia et al. (2017) consider the popularity of beverages in the UAE and note that the concentration of fluoride in Coca-Cola products is lower than that in Pepsi, its main competitor. Expanding the presence in the Middle East has become a valuable solution to driving sales. As a result, Coca-Cola’s business has a number of strengths that help the corporation maintain a leading position in its market segment.
At the same time, despite the advantages and strengths of the business, Coca-Cola’s activities are associated with some weaknesses. One of them is the potential harm to the body from the consumption of such products. According to Abbasi (2017), health care guidelines warn people about the negative effects of carbonated beverages high in sugar. Particularly, obesity and diabetes are real health threats, and to date, Coca-Cola has failed to address these factors successfully. The researcher also draws attention to underperforming water management and mentions cases of litigation in which the company was a defendant in cases of excessive water consumption (Abbasi, 2017). Moreover, in world practice, there are cases of pollution of water bodies with pesticides as a result of Coca-Cola’s industrial activities (Abbasi, 2017). In view of these weaknesses, the corporation has to work actively to interact with the population and carry out sustainable work in the face of constant restraints in the form of medical contraindications to the consumption of sugary beverages and accusations of inadequate resources management.
Among the opportunities open to Coca-Cola, one can mention the constant growth of sales markets and favorable conditions for collaborations with other companies. The corporation often acquires new brands in different regions, thereby strengthening its presence and ensuring successful control over market activity (Abbasi, 2017). In the Gulf countries, Coca-Cola’s presence is not as widespread as in some other world regions. This means that by interacting with local businesses and offering favorable terms for cooperation, the company can increase its credibility in the local market and achieve greater sales. In addition, by successfully overcoming the competitive barrier, the corporation can become the sole leader in its field since the current rivalry with Pepsi is a significant deterrent. Effectively addressing the logistics nuances of supply chains and transportation costs can help avoid unnecessary costs and deliver products to target markets, including the Middle East, more profitably.
Finally, the threats to the successful Coca-Cola business come primarily from high competition from Pepsi. Štofová and Kopčáková (2020) state that their rivalry has intensified since 2019 when Pepsi shares began to grow, and those of Coca-Cola, conversely, fell. One of the factors aggravating the situation for Coca-Cola is the lack of diversification of products since, in Pepsi, this criterion is more developed. Coca-Cola mainly offers only carbonated drinks, while Pepsi produces various snacks, which expands its target base of consumers (Štofová & Kopčáková, 2020). Threats to business from international environmental agencies are also emanating. Complaints about the use of plastic, environmental pollution, unsustainable resource management, and other aspects of production carry risks for the sustainability of Coca-Cola’s operations and maintaining brand loyalty. When taking into account the aforementioned constraints and prospects, the company should strengthen its work in several areas. Addressing competitive challenges by expanding the range of products and solving production difficulties are justified principles of strengthening Coca-Cola’s position both in the global market and in the Middle East. Therefore, the corporation should take into account various operational nuances and consider the requirements of modern green production principles.
The Eisenhower Matrix
The need for task planning explains the existence of various tools and schemes designed to facilitate the strategic assessment of the work ahead. One of such tools is the Eisenhower Matrix as a model that allows assessing the range of activities to be done visually based on the criteria of importance and urgency. According to Gray (2021), this framework that references President Dwight D. Eisenhower is comprehensive and can cover different contexts, be it business, research, or other projects. In a simpler explanation, this matrix implies assigning tasks in terms of their importance and urgency while taking into account the time frame and resources that may be involved. As Ruzevicius and Valiukaite (2017) note, this framework helps “find a balance between work and personal life” and may be utilized as a convenient planning algorithm (p. 79). From the standpoint of practical use, the matrix allows evaluating the range of upcoming tasks and demonstrates the best ways of implementing them. Such perspectives are valuable, and there are potential benefits to applying such a framework to personal work and research practice.
From my point of view, the importance of such a matrix is primarily due to the ability to categorize tasks to perform in accordance with the degree of their significance. While working on a specific project, this is sometimes difficult to assess the total volume of activities to complete and the objectives to realize in terms of their importance. This, in turn, can be a critical factor in determining how successfully and quickly specific tasks can be completed since an irrational approach to work is fraught with excess time and resources. I have compiled my individual matrix for the next two weeks, and it is shown in Figure 1. This diagram touches upon research on the analysis of Coca-Cola’s business and specific factors affecting the market success of the corporation. While working on this project, I should study a number of aspects, including operational nuances, competitive performance, product range, and other factors that affect the sustainability of the business. Sorting these tasks in accordance with their importance can help me do effective analytical work on time and without undue effort.
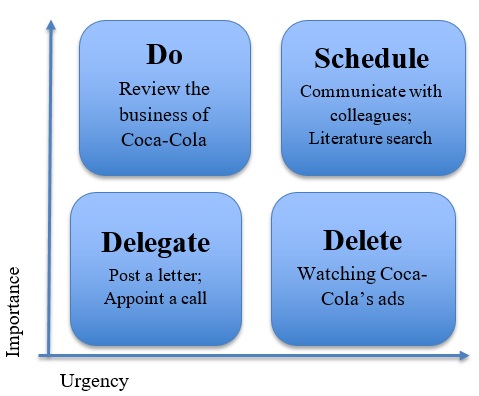
The most urgent and important task is to review and evaluate the specifics of Coca-Cola’s global operation and its unique marketing approaches, both internationally and regionally. The task that is less urgent but also important is the deep study of the proposed topic from an academic perspective. The analysis of primary data, search for credible findings, obtaining valuable information through communication, and some other procedures should be performed in the future. I can delegate some tasks successfully, thereby implementing my plans more quickly. Alternatively, I can call specific people or post a letter asking for individual visions of specific aspects. The least important work that also does not require urgency is the gradual study of media facts about the business in question. During the coming two weeks, I will be busy with my research, and the analysis of secondary and non-credible resources is not an important task. Thus, after compiling such a matrix, I can follow the outlined steps and achieve an optimal result. Productive work involves strategically sound interventions, and with this framework, my project will be completed successfully.
References
Abbasi, H. (2017). Marketing strategies of Coke: An overview. Kaav International Journal of Economics, Commerce & Business Management, 4, 194-199.
Gray, D. (2021). What makes successful frameworks rise above the rest. MIT Sloan Management Review, 62(4), 1-6.
Phadermrod, B., Crowder, R. M., & Wills, G. B. (2017). Importance-performance analysis based SWOT analysis. International Journal of Information Management, 44, 194-203.
Ruzevicius, J., & Valiukaite, J. (2017). Quality of life and quality of work life balance: Case study of public and private sectors of Lithuania. Calitatea, 18(157), 77-81.
Štofová, L., & Kopčáková, J. (2020). The competition strategy between Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi Company. Calitatea, 21(179), 40-46.
Walia, T., Fanas, S. A., Akbar, M., Eddin, J., & Adnan, M. (2017). Estimation of fluoride concentration in drinking water and common beverages in United Arab Emirates (UAE). The Saudi Dental Journal, 29(3), 117-122.