Industry Analysis
Industry Classification
Hyatt Hotel Corporation is an American multinational hotels and resorts company that operates in the luxury hotels and resorts niche of the hospitality industry. The most common properties are hotels, resorts and spas, fitness studios, and condominium ownership guests, which vary based on function, size, and cost. The market is segmented based on many factors, including facility type, geographical region, and the relative quality of services offered (Appendix A).
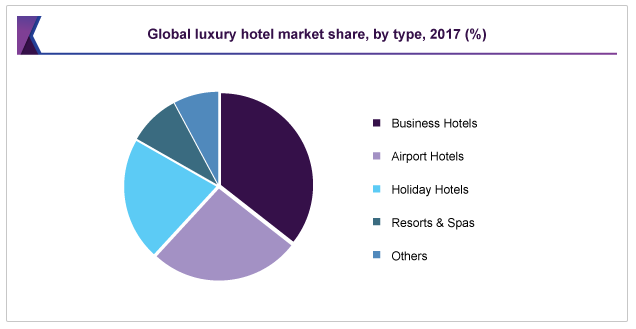
The main segments based on type include business hotels, airport hotels, holiday hotels, resort and spas, and others. Ass depicted in Appendix B, business hotels are the largest niche, accounting for approximately 35.0% of the global luxury hotel and resort sector (Grandview Research, 2018). Regional markets include North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Africa, the Middle East, India, and Central Asia. North America recorded the largest revenue share of over 35.0% in 2017 (Appendix C). The star-rating system is mains the most recognized measure of vertical differentiation in the hotel industry (Rajaguru & Hassanli, 2018). In light of this tool, industry players fall into six major categories based on the quality of the services they offer: 1, 2, 3. 4, and 5 Star.
Appendix D shows that Marriott International, Hilton Hotels, AccorHotels, Wyndham Hotel Group, and Hyatt Hotels are the leaders of multinational hotel companies with the highest revenue. However, revenue is not the only criterion for measuring the success of hotel companies. Other important figures, such as the number of properties, hotels, rooms, and employees should also be factored when the success of these corporations. In terms of hotels and rooms, for instance, the InterContinental Hotels Group PLC comes third ahead of the Wyndham Hotel Group other hotel chains with large revenues. Other dominant companies with well-established brands include Shangri-La Hotels and Resorts, Meliá Hotels International, InterContinental Hotels Group PLC, and NH Hotel Group.
The major strengths of the leading corporations include strong financial position and presence in multiple international markets. Marriott International and Hilton Hotels are the market leaders due to their strong financial position. Other primary sources of competitive advantage include strong brand recognition, higher level of customer satisfaction, high quality of services, amenities, and accommodations (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). Presence in international markets, diversified brand portfolios, and large revenue are other major strengths of hotel chains (Krupskyi et al., 2019). For example, industry giants, such as Marriott International and Hilton, operate in over 100 countries and territories.
Furthermore, most of the dominant players have dynamic marketing capabilities and rapid technological integration which serve as barriers to entry and neutralizes competition from small and independent operators (Krupskyi et al., 2019). For example, some corporations leverage advanced online travel and booking services to allow their clients to book stays on websites, consequently providing additional revenue and reputation. Lastly, strategic property locations enable some of the leading hotels and resorts to compete effectively (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). Companies such as Hyatt Hotels Corporation, Jin Jiang International Hotel Management Co., and NH Hotel Group, have branches in capital centers and near airlines, which facilitate access to the market.
Higher market concentration and scope of operation are perhaps the major weaknesses of the hotel and resort giants. A higher presence in the international markets exposes companies such as Hilton Hotel to unprecedented political, economic, and environmental risks and threats. Threats linked to economic recession and health crises (e.g., COVID-19 pandemic) may have several impacts on firms that operate in many geographical regions.
Hyatt hotels minimize such risks by focusing on high-end markets with a relatively strong economy. Another point of weakness of some of the giant hotel chains is high concentration in certain markets. Based on their research of 481 industries in the Australian economy, Leigh and Triggs (2016) found that some corporations exhibited a higher concentration in this market, with some firms commanding more than 80% of the local market share. The monopolistic competition result into fewer incentives to be efficient besides the possibility to restrict output onto the market.
Industry Size and Growth
The global luxury hotel and resort market was estimated to be $83.10 billion in 2017. The sector has witnessed depressed growth between 2013 and 2017 (Grandview Research, 2018). The North American market recorded poor financial performance, with revenue dropping from 36% to 32% (Grandview Research, 2018). The Asia-Pacific and Chinese regions reported a similar negative trend, with revenues dropping from 19.5% to 18.5% (Grandview Research, 2018). This poor performance can be attributed to the recent severe and prolonged downturn (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). The global market shares of tourism destinations plummeting during the 2013 recession (Perles-Ribes et al., 2016).
The depressed growth was exacerbated by other unfavorable economic conditions in major markets (such as North America and Asia Pacific), including low consumer confidence, heightened political instability, civil unrest, terrorist operations, and increased travel restrictions occasioned by terrorist threats, and oil crisis and instability (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019; Grandview Research, 2018). These data show that the luxury hotel and resort niche is very sensitive to radical changes and volatility in general economic conditions, such as economic crises.
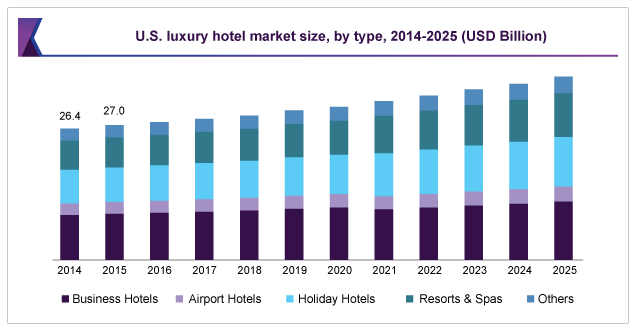
The global market for luxury hotels and resorts exhibited impressive performance compared to 2017. Amid the coronavirus pandemic, the hotel industry was valued at $174.9 billion in the year 2020 (Research and Markets, 2020). The U.S. commanded the largest market share in the luxury hotels niche, with an estimated value of $47.3 billion. The U.S., Europe, Canada, China, and Japan dominate the global Airport Hotels segment and account for a combined market size of $30.2 billion in the year 2020. This trend can be explained by the fact that these regions have the highest concentration of the leading hotels chains.
Despite the multiple headwinds, industry data show a relatively positive outlook on the part of the high-end hotel and resort market. The segment is projected to grow by a CAGR of 4.3% between 2018 and 2025 (Grandview Research, 2018). According to recent global luxury hotels market projection by Research and Markets (2020), the segment will grow at a CAGR of 2.6% between 2020 and 2027 to reach US$209.3 billion by 2027.
The Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate over the forecast period. China is anticipated to exhibit the fastest growth to hit $42.1 billion by the year 2027, driving a CAGR of 4.9%. To demonstrate this trend, Hyatt Hotels recorded an increase in their revenue, rising from $4.462 to $5.020 between 2017 and 2019 (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, and Canada are other regional markets other projected to experience high growth.
The impressive growth rate can be explained partly by the rise in purchasing power and general standards of living in several markets. As increased investment and injection of money into the economy results in a rise in the travel spending and demand for luxury accommodate for both business events and leisure trips. Besides that, some countries in Europe, for example UK, France, and Italy, have been increasingly investing resources in promoting their countries as tourism destinations. The special attention on the architectural or historical significance of such destination heightens the growth rate in luxury accommodation (Grandview Research, 2018).
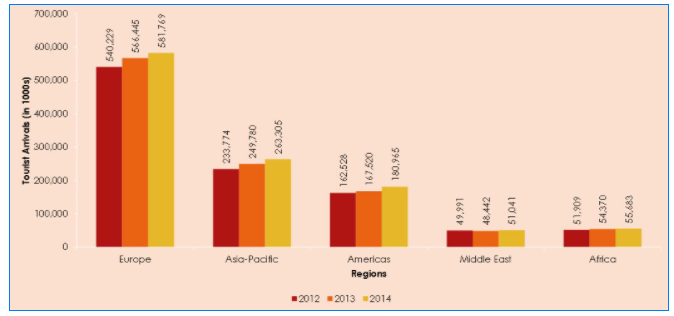
Lastly, Europe and several emerging economies, particularly China, India, Brazil, Thailand, and South Africa, are experiencing tourist arrivals (Appendix E). This trend is due to rising income of their population and is expected to heighten consumer purchasing power, which will consequently fuel growth and expansion of the luxury hotel and resort market. However, markets that are battling with political instability, civil unrest, economic crises, and unfavorable policies towards foreign direct investment (FDI) are predicted to experience declining or slow market growth (Grandview Research, 2018).
Overall, it is apparent that despite witnessing declining growth between 2013 and 2017, the luxury hotel and resort market is recovering gradually and the trend is anticipated to improve over the forecast period. The sector is likely to experience sustained growth as both individual and corporate consumers become more confident in relation to their rising disposable income and standard of living, coupled by the growing preference for leisure travel. These factors will spur significant increases in luxury travel rates and hotel room occupancy rates, which indicate the overall performance of the segment.
Government Regulations
Business establishments operating in the international luxury hotel and resort segment, and the hospitality industry in general, are subject to numerous laws and regulations at all levels of governance: local, state, federal, and international. The general areas that are highly impacted by those legal requirements include, sourcing, transportation, preparation, and sale of food and beverages, data privacy, business licensing, fair competition, building and zoning requirements, and environmental protection, among others (Hyatt Hotels Corporation,2019). For instance, all hotel business in different countries and regions are required by law to apply for business permits from regulatory agencies when they consider building, remodeling, refurbishing, or improving existing properties.
Furthermore, business enterprises in this niche are expected to run their business and operations in strict compliance with employment laws and regulations. Some of the legal issues related to the management of human resources relate to eligibility to work in a country, minimum wage requirements, workers’ safety and health, recruitment and selection, termination, discrimination based on protected classes, and compensation and benefits, among others. In the United States, for instance, the federal, state, and local enforcement agencies are mandated with administering and enforcing numerous laws to protect workers from exploitation, discrimination, and other work-related harm.
For instance, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibits high-end hotels and resorts from engaging in practices that may perpetuate any form of discrimination against employees and job applicants based on protected classes, including racial or ethnic background, age, faith, disability status, country of origin, pregnancy, and genetic information, among others (D’Angelo-Corker, 2021). In some jurisdictions, employers are required to comply with certain laws to develop and enforce policies aimed at protecting certain vulnerable groups (e.g., women and people living with disabilities) in the hotel industry from suffering sexual harassment. Complying with these labor standards helps to create workplaces free from wrongdoing by employers and colleagues.
Another legal standard that hotels are required to adhere to is mandatory financial and environmental reporting. Premium hotels and resorts, and other publicly traded corporations in the U.S. are expected to adopt the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to provide financial information that is relevant that can meet the unique decision-making needs of various stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and users.
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) framework requires business enterprises to produce accurate and useful information that reflect their financial position and performance, as well as any change in their financial position (Kawugana & Faruna, 2019). In addition, certain laws, regulations, and ordinances at all levels of governance require individuals and corporations that own or operate real properties facilities to protect the environment (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). For example, Hyatt Hotels may be held liable for costs incurred on investigation and remediation of toxic effluents they release into the environment.
The outbreak of coronavirus in early 2020 disrupted all businesses in the hospitality worldwide. The pandemic spread rapidly across international and national borders, with over 4.3 million and 290,000 people getting infected and succumbing to the disease by the end of 2020 (Nicola et al., 2020). The unprecedented escalation of this illness sparked widespread fears which not only discouraged local and international travels, but also necessitated governments to impose strict measures to ease the spread of the virus. Many hotels and other businesses shut down due unprecedented booking cancellations.
More than half of customers who participated in a recent survey said that they are not willing to travel to a destination and stay at a hotel any time soon (Gursoy & Chi, 2020). In addition to travel restrictions, hotels are required to comply with COVID-19 regulations, such as maintaining appropriate social distance, washing hands, regular using of soap, wearing facemasks, disinfecting surfaces such as tables, chairs, and other equipment regularly (Gursoy & Chi, 2020). These guidelines aim to ensure individual business premises cut the transmission and prevent the spread of COVID-19.
Noncompliance with applicable laws and regulations can be costly to companies in this sector. For instance, legal sanctions such as fines related to inaccurate reporting and release of harmful wastes into undesignated areas may affect the revenues, profits, and reputation of properties under the company’s management, license, ownership, or franchise. In this regard, hotels and resorts need to have a good understanding of government regulations that apply to their businesses to avoid such avoidable adverse consequences.
Company Profile
Hyatt Hotels Corporation is a multinational hotels and resorts company headquartered in Los Angeles, United States. The company was founded by Jay Pritzker, who bought the Hyatt House motel. The company changed its name to Global Hyatt Corporation in 2004 and Hyatt Hotels Corporation in 2009 after consolidating its businesses under a single entity. It went public in November 2009 following its deeply rooted tradition of innovation developed over its rich history that spans over 60 years. It is involved in the development, ownership, operation, management, franchising, licensing, and provision of services to a wide range of properties (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019).
Its range of services includes full-service, select-service, extended stay, and all-inclusive accommodations. Appendix F shows some of the most recognized brands owned by Hyatt Hotels. The company pursues aggressive growth and differentiation strategies focused on creating a strong customer base, building world-class brands, holding properties in strategic places, and building a robust development team to compete effectively and earn large profit margins.
Industry Classification
Hyatt Hotels Corporation operates in the travel and leisure niche of the international hospitality industry. In 2017, the market value of the global luxury hotel and resort market stood at an estimated $83.10 billion (Grandview Research, 2018).
The segment is characterized by intense competition from small-and-medium enterprises (SMEs), major hotel chains with established and recognized brands, small chains, independent property operators, and local owners and operators. Some of the dominant and primary competitors include Marriott International, Inc., Hilton Hotels, AccorHotels, Wyndham Hotel Group, and Jin Jiang International Hotel Management Co. Ltd. (Morris, 2017). Moreover, the hotel and resort niche is witnessing increasing rivalry from new channels of distribution and large firms that offer internet-based travel services such as Alibaba, Airbnb, and HomeAway (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). Unlike other competitors such as Hilton Hotels, which are present in almost every international market, Hyatt Hotels focus more on high-end travelers.
Size and Growth
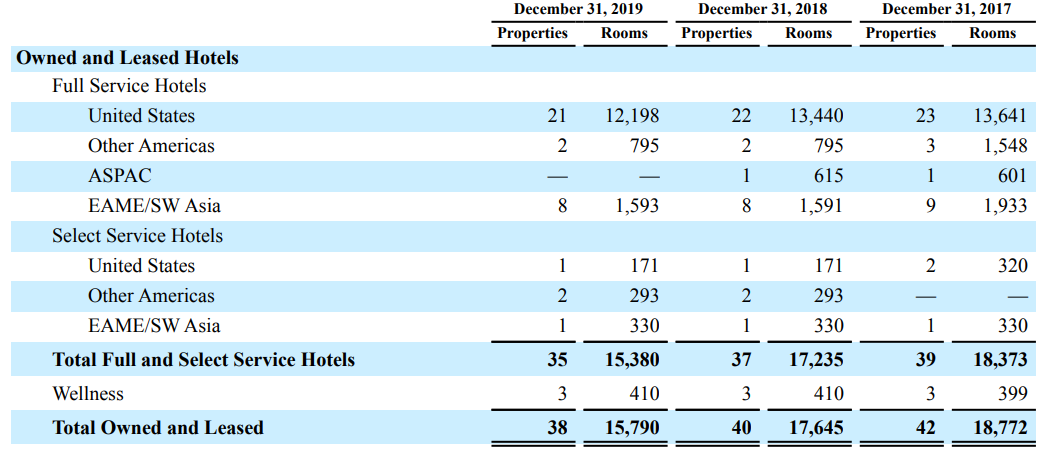
Since its establishment in 1954 as a single hotel adjacent to Los Angeles International Airport, the company has experienced dramatic growth and expansion to become one of the widely recognized brands in the high-end hotel and resort sector. By the end of December 2019, the corporation had a diversified portfolio totaling 913 hotels with 223,111 rooms and approximately 55,000 employees (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019).
The company’s revenue from both owned and leased hotels and resorts grew by $0,5 billion, from $4.5 billion to $5.0 billion for the years ended 2018 and 2019, respectively (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). The company dominates in major business centers and leisure destinations, such as London, New York, and Miami, due to their greater growth potential. Appendix G shows the four broad segments in which it operates and manages its businesses.
The company is committed to creating strategic acquisitions and alliances through its management and franchising model (Appendix H) to increase its global presence. The growth strategy is focused on acquiring brands that complement Hyatt Hotels Corporation’s ability to serve and satisfy the needs of their target high-end travelers. This is achieved by focusing on select locations, properties, and services. By the end of the year 2019, the company had a total of 38 properties which were either company-owned or leased. The company aims to heighten its international presence by penetrating new or existing under-penetrated international markets, including Spain, India, Iceland, Malaysia, Finland, and the Greater China, consisting of Beijing, Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Shenzhen.
Company Profitability
Factors Affecting Profitability
The competitive rivalry in the luxury hotel and resort market has a significant influence on the ability of Hyatt Hotels to make profit. In light of Porter’s five forces framework, analyzing the level of competitiveness in the market can help know whether firms can make profit (Varelas & Georgopoulos, 2017). The intensity of rivalry depends on the number of competitors in the given sector and the quality of their products and services.
Competition is a fundamental factor in the luxury hotel and resort niche due to the presence of aggressive competitors with well-established and globally recognized brands, such as Hilton Hotels and Marriott International. Hyatt Hotels is committed to creating a strong customer base, heightening its brand recognition, constructing properties in strategic places, and building a robust development team to compete effectively and earn large profit margins. Appendix I indicate that Hyatt Hotels has experienced impressive performance in the last one decade, enabling it to stay ahead of some of its competitors.
Another factor that has a significant impact on the profitability of Hyatt Hotels Corporation is seasonality. The hotel and resort sector, and the tourism and hospitality industry, in general, are inherently seasonal. Despite evolving rapidly to become a major contributor to national economies of different countries, the hospitality industry is adversely affected by seasonality due to the dramatic fluctuations in services demand. In their 2019 annual report, Hyatt Hotels Corporation (2019) presented a clear picture of the cyclical nature of this sector and how the peaks and troughs affect several performance outcomes, including demand for hotel rooms, luxury travel rates, and occupancy levels. Martin and Martinez (2019) document the actual consequences of the seasonality on the tourism sector.
The results of their investigation of entrepreneurs’ attitudes toward the cyclical patterns based on two tourist destinations in Spain showed that prolonged off-peak seasons have severe impact on the demand, consequently leading to closure to some establishments. The low demand and shutting down during low seasons are detrimental to the profitability of Hyatt Hotels Corporations in terms of declining revenues and sales during off-peak seasons. Therefore, Hyatt Hotels Corporation and other industry players have to explore innovative ways to offset the adverse effects of the seasonality.
A company’s market position (reputational, financial, and geographical) has a marked influence on its profitability. This factor is well demonstrated by Hyatt Hotels Corporation’s strong position in terms of its financial stability, brand recognition, and strategic location. The multinational hotel chain operates in many major cities. Its hotels, resorts, and other properties are strategically located near ports of entry (e.g., airports, sea ports, and railway stations), which make them more accessible to customers. Besides that, the company’s brands such as (Hyatt, Hyatt Regency, Hyatt Ziva, Hyatt Zilara, Hyatt Centric, and Thompson Hotels) enjoy global recognition (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). The strong brand reputation contributes to the firm’s profitability by creating stronger attraction and demand.
Diversification is another critical contributor to profitability in the luxury hotel and resort sector. Appendix I demonstrates how Hyatt Hotels Corporation pursues strategic acquisitions and alliances to penetrate new markets and expand their global presence (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). In addition to the corporate headquarters, the company has properties and hotels in all the four geographical segments, which help in maintaining its global presence. Besides that, Hyatt Hotels leverages its aggressive entry growth to entry into new unexplored markets while also introducing a new product into that area.
It offers a variety of high quality properties and services in strategic locations, a tactic that supports its objective of achieving unmatched customer preference (Hyatt Hotels Corporation). For example, between 2009 and 2019, the hotel chain penetrated a total of 281 new markets and 24 new countries (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). In 2019, it launched several loyalty collaborations with established partners, such as American Airlines and Lindblad Expeditions. These strategic acquisitions help bolster the company’s capability to serve their existing customer base.
However, the product and geographical diversification expose the company to a wider investment opportunity which enables the giant to exploit more profitable investment projects (Jouida, 2018). This would be impossible if the company focused on a single market like North America. Besides that, this growth strategy allows the corporation to reduce transaction costs and take advantage of other economies of scope (Jouida, 2018). Lastly, spreading the risk across different brands and markets minimizes the risk of loss. For example, higher performance in Asia Pacific may offset the negative impacts of declining growth, sales, and profit in more saturated markets such as Europe and North America.
Lastly, marketing capabilities are another primary driver of profitability in the tourism and hospitality industry. Hyatt Hotels Corporation’s strong brand recognition can be attributed to the company’s aggressive marketing strategies. The firm targets its marketing and promotional campaigns on the premium traveler, a tactic that allows them to position themselves as a leading brand in each segment in which they operate. The innovative marketing initiatives help the hotel chain to build and differentiate its brands, which is critical to heightening their brand presence, maintaining current customers and attracting prospects, and making more sales and profit.
Product Differentiation
Hyatt Hotels Corporation pursues product differentiation strategy to compete effectively with fierce rivals such as Hilton Hotels, Marriott International, Inc., and Wyndham Hotel Group. The multinational targets the luxury market segments with their innovative marketing and loyalty programs (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). Offering uniquely differentiated services in high-end, upper-upscale hotels and resorts, enables the firm to not only provide unique customer service and experience but also satisfy needs and wants of their target segments. Moreover, the limited focus on the premium consumers allows the business to position its brands among the top competitors in each segment in which it operates.
The strong fidelity to the high-end clients helps in driving stronger loyalty and community, which scale up its brand presence. It leverages advanced technological applications such as data analytics to learn and understand trends in consumer needs and preferences, and ways of addressing the changes in the distinct guest segments they serve.
Degree of Company Concentration
Hyatt Hotels Corporation exhibits a relatively higher concentration in the markets and segments in which it operates. By the end of fiscal year 2019, the multinational held a total of 38 properties (both company owned and leased) and 26 managed or franchised properties (Hyatt Hotels Corporation, 2019). The company’s concentration can be justified by its high presence in specific segments, especially key markets such as major business centers and leisure-based destinations. The company is increasingly shifting from concentrated markets, especially busy towns and cities, including New York, London, Paris, Miami, and Zurich.
The higher presence in these particular areas provides strong evidence for its concentration. In an attempt to achieve greater growth and international presence, the company is entering new, emerging and dynamic markets with stronger growth potential, such as India, South Africa, Brazil, and Great China. These areas remain relatively under-penetrated compared to their saturated counterparts in Europe and Americas, thus they hold greater opportunity to drive preference for the Hyatt brands.
Price Factors
Despite the fact that Hyatt Hotels Corporation enjoys stronger brand recognition and reputation, higher level of customer satisfaction, high quality of services, amenities, and accommodations, the relative price of its services remain a key consideration. Price affects many variables, including market growth, level of competitiveness in the market, brand reputation, and company profitability. Many internal and external factors impact the company’s premium pricing strategy. Some of the prominent factors include prices charged by competitors, and costs incurred on procuring supplies, such as raw materials, food, equipment, and furniture, paying employees, obtaining business permits, and other fixed and variable expenses.
The main objective of every business enterprise is to earn sustainable profit. Consequently, Hyatt Hotels Corporation considers the both fixed and variable costs and prices charged by competitors when setting their prices in order to remain profitable. Besides that, the demand and supply affect the company’s pricing. For example, it charges higher prices for its services during peak seasons due to heightened demand for luxury travel and accommodations, and reduces it during off-peak period. These tactics allow the enterprise to remain profitable in the long-term.
References
Alarussi, A. S., & Alhaderi, S. M. (2018). Factors affecting profitability in Malaysia. Journal of Economic Studies, 45(3), 442-458. Web.
D’Angelo-Corker, K. (2021). Time to Panic! The need for state laws mandating panic buttons and anti-sexual harassment policies to protect vulnerable employees in the hotel industry. Seattle University Law Review, 44(2), 229.
Grandview Research. (2018). Luxury hotel market size, share & trends analysis report by hotel type (business, airport, holiday, resort & spa), by region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Mea, Latin America), and segment forecasts, 2018 – 2025. Web.
Gursoy, D., & Chi, C. G. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on hospitality industry: review of the current situations and a research agenda. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 29(5), 527-529. Web.
Hyatt Hotels Corporation. (2019). 2019 annual report on form 10-K [PDF document]. Web.
Jouida, S. (2018). Diversification, capital structure and profitability: A panel VAR approach. Research in International Business and Finance, 45, 243-256. Web.
Kawugana, A., & Faruna, F. S. (2019). Role of financial statement in investment decision making. International Journal in Management & Social Science, 7(1), 87-99.
Krupskyi, O. P., Dzhusov, O., Meshko, N., Britchenko, I., & Prytykin, A. (2019). Key sources when formulating competitive advantages for hotel chains. Tourism: An International Interdisciplinary Journal, 67(1), 34-46.
Leigh, A., & Triggs, A. (2016). Markets, monopolies and moguls: The relationship between inequality and competition. Australian Economic Review, 49(4), 389-412.
Martin, J. M. M., & Martinez, J. M. G. (2019). Entrepreneurs’ attitudes toward seasonality in the tourism sector. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research, 26(3), 432-448. Web.
Morris, J. (2017). Top 10 leading hotel groups. Web.
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C.,… & Agha, R. (2020). The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus and COVID-19 pandemic: a review. International journal of surgery, 78(),185-193. Web.
Perles-Ribes, J. F., Ramón-Rodríguez, A. B., Sevilla-Jiménez, M., & Rubia, A. (2016). The effects of economic crises on tourism success: An integrated model. Tourism Economics, 22(2), 417-447. Web.
Rajaguru, R. and Hassanli, N. (2018). The role of trip purpose and hotel star rating on guests’ satisfaction and WOM. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 30(5), 2268-2286. Web.
Research and Markets (2020). Global Luxury Hotels Industry (2020 to 2027) – Market Trajectory & Analytics. GlobalNewswire. Web.
Varelas, S., & Georgopoulos, N. (2017). Porter’s competitive forces in the modern globalized hospitality sector–the case of a Greek tourism destination. J Tour Res, 18, 121-131.
Appendices
Appendix D: Leading Hotels and Resorts by Size.
Appendix F: Top Hyatt Hotels Brands.
Appendix G: Hyatt Hotels Market Segmentation.