- Introduction: Specifics of the Saudi Arabian Market Economy
- Increase in Market Demand and Sales Quantity
- Rise in Prices due to the Reputation Growth
- Reduction in Costs Due to Increased Efficiency
- Increase in Productivity
- Reduction in Future Costs as a Result of Environmental Control
- Conclusion: Opportunities for the Saudi Arabian Markets
- References
Introduction: Specifics of the Saudi Arabian Market Economy
The economic landscape of Saudi Arabia is complex in its ties between the government and the private entrepreneurship. Supervised extensively in most of its domains by the government, the Saudi Arabia market can be viewed as a highly functioning mechanism that is based on the efficacy of the oil and gas industry efficacy for the most part. According to the latest statistical reports about the progress of the Saudi Arabian market, however, there has been a significant increase in the efficiency of open markets; particularly, the trade freedom rates peaked at 77.8%, which is an impressive achievement. The investment and financial freedom remain at modest rates of 40% and 50% correspondingly (Saudi Arabia, 2016).
Because of the high market benefit rates spurred by the efficacy of the companies operating in the oil and gas industry (especially crude oil production), the speed of the economic growth rates is becoming increasingly high in the Saudi Arabian environment.
Increase in Market Demand and Sales Quantity
As stressed above, the performance of the organizations operating in the oil and gas industry has an especially significant impact on the characteristics of the Saudi Arabian market. Therefore, it will be necessary to look closer at some of the changes that the identified domain of the Saudi Arabian market has suffered recently. Because of the consistent rise in the market demand for crude oil and the related products, the sales quantity has been on the rise since 2015 (with minor hiccups in autumn 20915 and winter 2016) (see Fig. 1). Thus, demand and sales rates have a direct effect on economic growth rates.
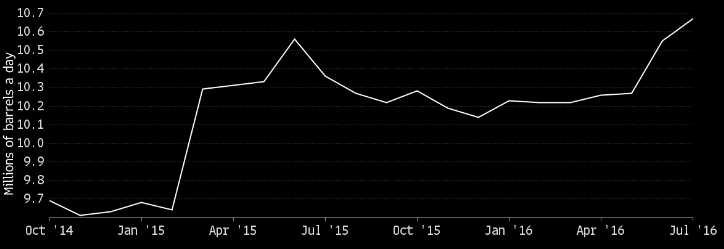
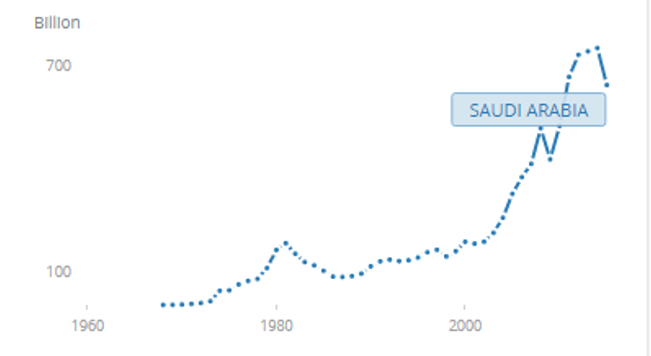
The state GDP, in its turn, seems to correlate with the changes in the market demand and the sales quantity (see Fig. 2). Therefore, it can be assumed that the identified factor has a direct effect on the development of the Saudi Arabian economy. As the graphs provided above and below show, there is a direct correlation between the identified variables. With the increase in demand for crude oil, which can be witnessed currently, the economic growth rate also rises.
Rise in Prices due to the Reputation Growth
When entering the global market, one must not underrate the gravity of having a poor reputation. The consequences of failing to prove the state to be economically, technologically, and culturally advanced is likely to cause an immediate drop in the number of customers and the failure to establish a presence in the global market. Building the image that appeals to the target audience is, on the contrary, the pathway to success, as the example of Saudi Arabia shows.
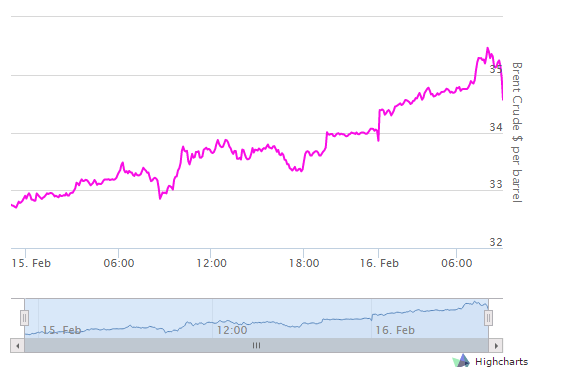
The state authorities have been striving to make an impression of a thriving economy, which led them to dismiss Doha as one of their potential partner in trade (Khan, 2016). Remarkably, the changes in the policy of the state and the subsequent dismissal of certain trade partners do not necessarily lead to immediate improvement. As the latest data on the economic well-being of Saudi Arabia shows, the drop in oil production that was witnessed in February can be deemed as a threat to the consistency of the economic progress of the state (see Fig. 4).
Reduction in Costs Due to Increased Efficiency
A drop in expenses that comes as a result of an increased performance rate can be viewed as one of the factors driving the Saudi Arabian economy upward. The identified process is especially important in the environment of the global economy with its price hikes. For example, the Saudi Arabian fertilizing companies have recently been using cost-efficient approaches to bring down the percentage of expenses. Thus, they increased their revenue streak (Alperowicz, 2016).
Increase in Productivity
The rates of services and goods production are also viewed as an essential indicator of the state’s market development, and Saudi Arabia is no exception to this rule. Although the oil industry seems to be a graphic example of the identified phenomenon, other domains of the state economy also display similar tendencies. For instance, the transportation industry, in general, and the air travel area, in particular, show a tendency for an increase in productivity, which affects the Saudi Arabian market in a rather positive way. As Fig. 3 shows, the contribution of the revenues retrieved from the air travel domain to the state GDP can be defined as not only impressive but also increasingly large.
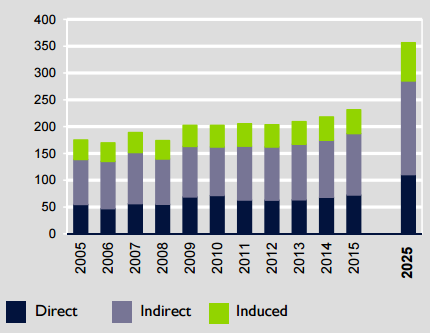
Therefore, the air travel data, as well as the tourism industry statistics, in general, points directly to the correlation between the market benefits and the economic growth in Saudi Arabia. The Saudi Arabia Airlines, which is ranked among the top three most influential organizations in the state (Yaghi & Sindi, 2016), is currently in debt to the government (Trading Economics, 2016). However, its potential is truly immense. Thus, the performance of the organization affects the economic growth of Saudi Arabia.
Reduction in Future Costs as a Result of Environmental Control
Finally, a drop in future expenses needs to be mentioned as the force that has a tangible effect on the Saudi Arabian market. The effects of the identified characteristic of the target economic environment, however, may be viewed as somewhat dubious. On the one hand, the reduction in the costs spent as a means of maintaining environmental stability is a positive change. However, a recent report shows that the total possible revenue of $20,000,000,000 was not retrieved due to the implementation of cost-cutting policies in the state (Bianchi, Fattah, & Martin, 2016).
It could be argued that the effects of the identified approach toward managing the state resources are likely to have positive long-term effects on economic growth. After all, complying with the essential environmental principles will help Saudi Arabia gain an even better reputation in the environment of the global market. As a result, prerequisites for an even more successful economic performance can be expected. Nevertheless, the state authorities must also pay closer attention to the outcomes of their decisions in the context of the local corporations and SMEs.
Conclusion: Opportunities for the Saudi Arabian Markets
Market benefits have a significant impact on the performance that different states deliver in the environment of the global economy. Although Saudi Arabia has been enjoying the benefits of the global market such as an increase in market demand, a drop in costs, etc., it will have to adjust to the global market realm to make proper use of these advantages. Furthermore, it is necessary to bear in mind that some of the factors may have not only positive but also negative impacts on the Saudi Arabian economy, such as cost reduction that comes at the price of promising projects. Once the essential factors are taken into consideration, the state will be represented in the global market appropriately.
References
Alperowicz, N. (2016). Saudi firms reducing costs to soften blow of feedstock and energy hikes. IHS Chemical week. Web.
Bianchi, S., Fattah, Z., & Martin, M. (2016). Saudi cost-cutting drive may cancel $20 billion of projects. Bloomberg. Web.
Khan, M. (2016). Oil prices crash after Saudis fail to broker global production cut. The Telegraph. Web.
Saudi Arabia. (2016). Web.
Trading Economics. (2016). Saudi Arabia government revenues. Web.
The World Bank. (2016). Saudi Arabia. Web.
World Travel and Tourism Council. (2014). Travel & tourism. Economic impact 2015: Saudi Arabia. Web.
Yaghi, K., & Sindi, Y. O. (2016). Importance of knowledge management in establishing organization strategy: Study on Saudi Arabian Airlines HR Division, Jeddah. International Journal of Business and Management, 11(3), 235-247. Web.