Introduction
The grocery store segment highly depends on the levels of customer satisfaction. To stay competitive in their segment, grocery store chains must be highly attractive to potential clients. Tesco is a British retail chain specializing in groceries and other merchandise and is the third-largest multinational retailer worldwide, with locations in America, Asia, and Europe. Due to the flexibility that supermarkets offer, Tesco has been capable of diversifying its products and services and attracting customers who keep returning and purchasing from the stores. Thus, starting out as an exclusively grocery store chain, Tesco has engaged in significant diversification over the decades of its operations. The aim of this paper is to discover the strategies that Tesco has employed to attract its clients and become one of the leaders in its segment. The objectives are the following:
- To explore Tesco’s marketing mix as an indicator of the appeal that the company provides to customers;
- To evaluate Tesco’s marketing strategy to reveal how the company targets its potential customers;
- To evaluate the internal and external factors that allow Tesco to stay competitive and attract and retain clients over the years.
The main issue related to the current study is concerned with understanding the strategies that grocery store giants such as Tesco use to stay competitive for decades. The grocery store market is highly competitive, with high barriers to entry, and it is demanding for brands to remain relevant on a long-term basis due to the continuous changes in customers’ expectations and demands. Tesco’s case can be used to determine the keys to success in the industry. The research questions are as follows:
- How does Tesco market its products to make them appealing to customers?
- Is the pricing strategy relevant to the company’s attractiveness among clients?
- Are there any particular strategies associated with sales and promotions?
- Overall, how does Tesco manage to maintain its position in the competitive market?
Literature Review
Researchers have cited the example of Tesco as a company that has, despite the challenges, have managed to stay relevant for decades and maintain its customers (Hanson et al., 2017). The company’s vision has consistently been maintained, with the focus on being wanted and needed by customers worldwide (Ward Howell International, no date). The key to success has been Tesco’s approach to its marketing mix (Lynch, 2018). Notably, since its inception, the company has expanded its product range beyond food to include clothing, electronics, home and décor, beauty products, baby products, and many others (Vasquez-Nicholson, 2016; Eley, 2020). While the product strategy has allowed covering the various needs of customers, its pricing strategy has been focusing on offering the lowest prices possible without compromising on quality (Shastri, 2022; Sarkar, 2021). The cost leadership strategy at Tesco has allowed to reduce irrelevant costs and listen to customers regularly.
While the pricing strategy allows for Tesco to be quite appealing, the company has been vastly using print and media advertising as core channels for sending promotional messaging to customers (Faull, 2021). The ‘buy one get one’ promotions have been particularly popular alongside with club cards (Brignall & Smithers, 2019). At the core of Tesco’s marketing strategy lies a well-positioned brand image that targets cost-conscious consumers who are interested in variety, promotional offers, and sales (Kar, Bansal, & Mishra, 2021). Such positioning has allowed Tesco to find the ‘middle ground between offering affordable products while having the broadest range from which customers can choose (Cascade Team, 2021). Internally, Tesco has been successful at building an efficient supply chain network (Donati, 2021), which can allow it to externally expand to emerging markets in the future (Business Strategy Insights, 2021). Despite facing competition from such companies as Lidl, ASDA, Aldi, and Walmart, Tesco has engaged in strategic alliances with other brands to appeal to more customers (Downie, 2021; Potter, 2011). It is expected that the competition will remain strong for upcoming years, which means that Tesco will have to strengthen its alliances.
Methodology
To answer the research questions identified previously, the literature review methodology appears the most appropriate. A literature review is a qualitative research methodology involving researching, evaluating, and summarizing literature about the topic at hand. The approach allows one to stay up-to-date with the latest research on the chosen issue and assess available evidence and the implications it presents for future studies (Snyder, 2019). In this particular study, the literature review methodology is used for evaluating the state of knowledge on the chosen topic. The overview of the evidence will help create research agendas and discuss the particular matter. Moreover, the method can be instrumental to theory development.
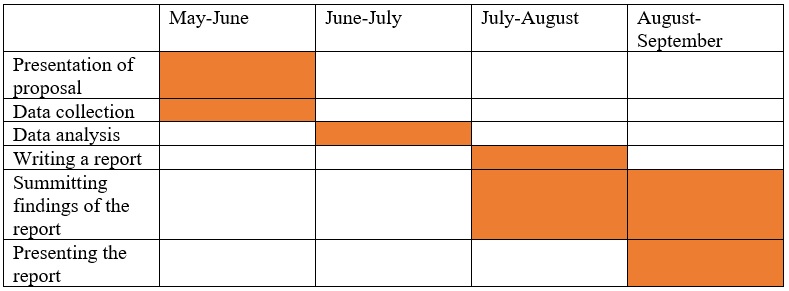
Integrating the results of the review, thematic analysis can be used, which is a method of finding patterns and trends in data that allow for making conclusions from the collected information. The information to be included in the literature review was gathered using an online search on Google and Google Scholar. While preference is given to published books and peer-reviewed research articles, there are not enough published works that discuss Tesco’s strategy of attracting customers. Therefore, information from reputable websites, excluding Wikipedia and other similar platforms, could be included in the analysis. The chart below (Table 1) shows a timeline for project completion:
Findings
The review of literature on the strategies that Tesco implements to attract customers and maintain them long-term revealed several significant findings. They are presented in the table below, which breaks down findings based on research questions (Table 2).
Table 2. Literature review findings (Self-generated).
The findings of the literature review on how Tesco attracts its clients show that the company has worked for decades to find the approach that is the most suitable for its goals. While groceries are an essential segment, the company’s management has realized that customers need variety to keep being interested in going to Tesco on a regular basis. The expansion and diversification of the product range have been instrumental in getting more customers interested in Tesco because they could purchase anything they need in one place. With the help of the price leadership strategy, regular promotions and bonuses of the club card, customers get a multitude of benefits when shopping at Tesco. The company faces tough competition from grocery store rivals but implements such strategies as strategic alliance and diversification to stand out from them.
Conclusion
To conclude, the key to the competitiveness of a company operating in the grocery store segment is the attentiveness to customers’ needs and expectations. Tesco is an example of how to successfully attract and retain customers by being in tune with what they want to find at their local supermarket. The combination of product diversification and cost leadership has put the company on a pedestal of a high standard when it comes to serving customers’ needs. Due to the industry’s competitiveness, it has shown that a grocery store company can only stay relevant when it is up-to-date with the latest trends and can be flexible within its strategy.
Reference List
Brignall, M. and Smithers, R. (2019) ‘Tesco clubcard plus: is the new £8-a-month deal worth it?’ The Guardian.
Business Strategy Insights. (2021) Tesco’s SWOT analysis.
Cascade Team. (2021) How Tesco became the biggest retailer in the UK.
Donati, M. (2021) Tesco’s supply chain helps it ‘outperform’ the market.
Downie, R. (2021) Who are Tesco’s main competitors?
Eley, J. (2020) ‘How Dave Lewis fixed ailing supermarket giant Tesco,’ Financial Times.
Faull, J. (2021) Tesco has a major new media offering for advertisers: here’s what you need to know. .
Hanson, D. et al. (2017) Strategic management: competitiveness and globalization. Melbourne: Cengage Learning.
Kar, S. K., Bansal, R. and Mishra, S. (2021) ‘Tesco: entry and expansion strategy in India’, Emerging Economies Cases Journal, 3(2), pp. 65-76.
Lynch, R. (2018) Strategic management. 8th edn. New York: Pearson Education.
Potter, M. (2011) ‘Tesco brands to lure aspirational shoppers’, Reuters.
Sarkar, M. (2021) TESCO – British retailer that redefined grocery shopping.
Shastri, A. (2022) Step-wise marketing mix of Tesco with complete 4Ps and overview.
Snyder, H. (2019) ‘Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines’, Journal of Business Research, 104, pp. 333-339.
Vasquez-Nicholson, J. (2016) UK supermarket chain profiles 2016.
Ward Howell International. (n.d.) Tesco. Vision, values, and business strategies. Web.