The Subject/Issue
Owing to increased liberalization and globalization, employees have become a competitive advantage for most organizations. Proficiency is indispensable to every triumphant enterprise. Similarly, incompetent employees are a recipe for failure to any enterprise. Today’s labor market is very tight. As a result, businesses have realized the importance of keeping their best employees by instilling and developing employee loyalty.
However, this task continues to pose a major challenge that necessitates many organizations to formulate their human resource strategies and/or policies, which foster employee loyalty. This process often entails allocating enough resources that keep the employees contented and motivated to continue working for the organization at their level best. This paper seeks to investigate various strategies that boost employee loyalty strategies by businesses and the impact of effective human resource allocation policies on employee loyalty.
Problem Statement
Employee loyalty in the workplace remains a considerable challenge in most businesses today with many of them facing problems regarding the retention of their most competent employees. Therefore, organizations, particularly human resource management departments, have the responsibility to know how to attract and retain the organization’s best employees through increasing their workplace loyalty.
The main causes of the declining loyalty of employees towards their organizations include lack of connection with their responsibilities/duties in the organization, lack of employee motivation, negative attitudes by employees, and stressful work environment. Other causes include misallocation of duties, lack of potential growth in organization, lack of recognition and appreciation in the form of incentives, and underutilization of employee knowledge and skills (Murope and Bangi 13).
In addition, most organizations lack a system that can measure the extent of loyalty of employees towards the firm. In fact, most firms have no clue of the extent of their employee alignment and retention problems. For instance, while older employees between the ages of 35 to 50 years have a lower turnover rate, employees aged between 25 and 34 (mostly fresh graduates) have the highest turnover rate.
Despite being the most productive cohort, employees within the later age bracket are considered the least loyal and the most non-aligned regarding the corporate strategy. Therefore, they are at the greatest risk of deflection from the organization. Therefore, besides increasing their loyalty by reducing the causes of low employee loyalty, organizations also need to devise creative ways of measuring loyalty among their employees, especially workers at the lower age bracket, to decrease the rate of employee turnover and/or retain their most productive personnel (Ong 93).
Problem Justification
Recent studies such as the study by Ong among others continue to affirm the state of high employee turnover in various companies from various sectors in the US (93). Most of these studies indicate that most of the employees, particularly between age 25 and 35, are moving from one company to another seeking better terms of employment. For example, research carried out by The US Bureau of Labor Statistics indicated an increase in the number of hires to close to 5.5 million in 2016, an increase of roughly 300,000 recruits in the previous year (par.1).
This figure is also recorded as the highest hire rate since November 2006. Moreover, the research also revealed a higher rate among private companies compared to local government organizations. Among the reasons for organizational separation included layoffs, discharges, and quits. In this regard, the number of organizational separation was recorded at a high of 5.1 million with the largest portion of approximately three million being attributed to quitting.
Give up here denotes deliberate disconnection that is initiated by the workers themselves. Therefore, the high level of quitting can be used to indicate a low level of employee loyalty to their organization, which causes them to leave their current workplaces (The US Bureau of Labor Statistics par.2). From the above statistics, it can be deduced that a study of the impact of specific strategies by various successful organizations would be prudent in driving their integration in struggling organizations with the overall positive effect of reducing high employee turnover in this caliber of organizations.
Study Hypotheses
After determining dependent and independent variables of the study, the following study hypotheses were developed:
Study Hypotheses
- Hypothesis 1. A significant direct relationship is evident between low employee loyalty and high employee turnover rate. Therefore, low employee loyalty is associated with a high rate of turnover and vice versa.
- Hypothesis 2. Low employee loyalty is caused by low job satisfaction, lack of a potential growth within the organization, underutilization of employee skills and knowledge, misallocation of duties by an employee, stressful work environment, and negative attitudes of employees towards the organization, including lack of recognition by the employer through effective reward systems.
- Hypothesis 3. Companies that have effective human resource policies and/strategies, which eliminate or mitigate the causes of low employee loyalty are effective and hence have low turnover rates and high organizational commitments.
Introduction
Employees represent a crucial resource for most organizations. Therefore, they represent an important investment in reference to recruiting, identifying, training, bonuses, healthcare plans, insurance plans, and salaries. The human resource management is responsible for developing training programs, performance appraisals, bonuses, work systems, and other benefit packages through adhering to the company’s human resource policies/strategies.
Such policies are objected at instilling and developing loyalty among a firm’s employees with the ultimate effect of more prolonged employee work tenure. Therefore, worker devotion can be regarded as the personal pledge of a member of staff to the victory of a business with the conviction that serving in the business is the most favorable and desirable alternative. Quite often, employee loyalty is linked to organizational commitment, which is an organizational behavior or attitude that is reflective of an employee’s loyalty towards their organization. Thus, employees who are loyal to an organization will exhibit a high level of commitment to the achievement of organizational objectives.
Additionally, devoted workers trust that being part of a business is the most favorable opportunity. Thus, they are less likely to deflect to other organizations in search of greener pastures. In an effort to maintain competent employees, the paper shows how successful organizations formulate effective human resource strategies and/or policies that eliminate negative workplace attitude associated with low level of loyalty while fostering employee satisfaction and loyalty among their workforce. This way, these organizations record a low turnover rate and higher job performances.
Literature Review
According to Alrawabdeh, employee loyalty has a huge impact on the level of performance of any member of staff (119). Such insight has led many organizations to seek ways of improving the level of loyalty among their employees through formulating effective strategies and policies linked to the enhancement of the performance of human resources. Additionally, organizations strive to compete for the best available human resources to ensure that their most competent workforce is retained.
As a result, firms are continuously developing new creative approaches such as internal marketing, performance appraisal, reward management, and performance recognition programs that focus on the development and motivation of employees in an effort to enhance the level of employee loyalty, job satisfaction, and performance. Such positive staff attributes positively reflect in the form of high quality of service, high customer loyalty, and high financial performance by an organization (Alrawabdeh 119). They offer the business a competitive advantage.
Contrary to popular belief, Wan reports that money is not among the causes of low loyalty and high employee turnover (5). In fact, organizations that spend more time attending to their employees’ welfare have shown to portray a higher level of employee loyalty and performance (Wan 6). The main drivers of high employee loyalty include job satisfaction, respect in the workplace, the potential for career growth, employee reputation, employee recognition, high level of concern for employees, and high level of trust by the employer, just to mention a few.
A survey reported by Wan indicated that employees in the public sector illustrated a higher level of employee loyalty and consequently had a lower turnover compared to the private sector (6). This situation was mainly attributed to the high level of teamwork exhibited among workers in the public sector. This case notwithstanding, the following factors were also attributed to high level of employee loyalty: open communication, competitive pay, favorable working atmosphere, potential for career growth, and taking care of employees’ welfare, for instance, health and insurance, availing training opportunities, and high-level engagement of employees to the organizational activities.
Similarly, a study carried out by Ong among fresh graduates marked organizational factors and attitude as the main factors affecting employee loyalty (103). Moreover, the research identified that lack of job satisfaction was grossly associated with low loyalty and high turnover. In addition, high salary and level of occupation were not among the essential factors regarding job satisfaction and workplace loyalty. According to the study results, self-determination towards work, organizational rewards system, life-work intimacy, and personal responsibility towards the job showed a positive effect towards the creation of job satisfaction and employee loyalty (Ong 103).
Based on theories of employee loyalty, Martensen and Grønholdt developed a conceptual model to illustrate the relationship between the determinants and the impact of employee loyalty on an organizational setting (94).
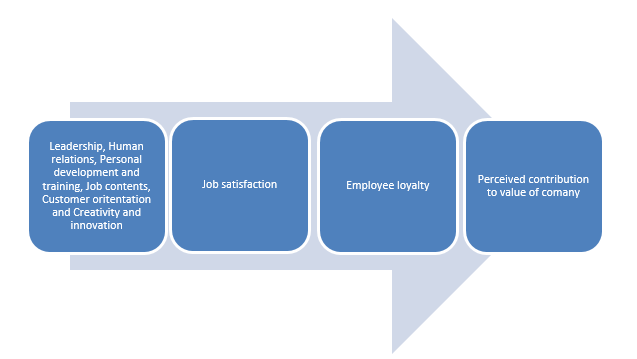
In this model, leadership, personal development, training, job contents, creativity, and innovation are considered the determinants of job satisfaction and employee loyalty while job satisfaction, employee loyalty, and the perceived contribution to the company are viewed as results that emanate from the effective practice of the determining factors. Therefore, the presence of good leadership, positive human relations, potential for personal development through training, and employee engagement through the encouragement of creativity and innovation have a positive impact on job satisfaction, employee loyalty, and the superficial employee contribution to the value of the company.
Research Methodology
Data Gathering
The study design was a descriptive study that was based on primary data collected through issuing of questionnaires to the study population. The study participants included employees and human resource management staff of various organizations selected from several states in the US. The questionnaires investigated the level of employee loyalty, its close association with organizational commitment and job performance of the organizational staff, and the attitudes of various employees towards various human resource strategies and/or policies implemented by their respective organizations. Regarding the sample size, 300 participants, both employees and human resource staff, were randomly selected from 50 organizations.
Data Entry and Analysis
The data collected was analyzed using SPSS software. This package covers a wide range of statistical procedures. In addition, it allows the researcher to analyze the data collected to determine the presence/absence of significant differences and/or relationships among various selected groups participating in the study. In this case, five independent variables that represented the various human resource strategies and policies used by organizations to foster employee loyalty were identified.
They included employee engagement, reward and performance appraisal systems, a favorable/conducive work environment, employee development and training, and open communication. Their effects were then compared against the dependent variables represented by the levels of employee loyalty and job performance. The effect of each of the independent variables on the dependent variables was measured using impact scores ranging from 0 to 1 with the total score/effect of all the variables totaling to 1.
Results
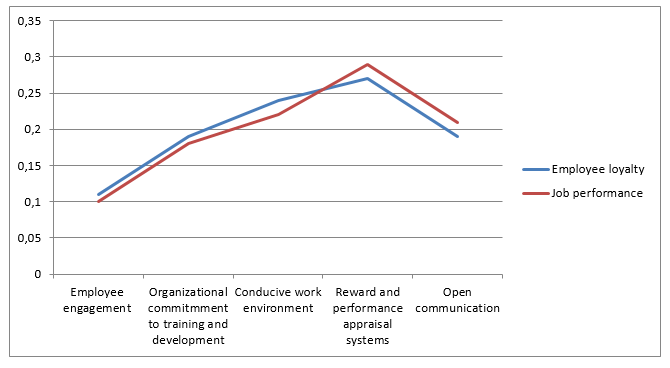
Table 1: The Impact scores of Human Resource Strategies/Policies (Independent Variables) on Employee Loyalty and Job Performance.
Discussion
The empirical evidence presented by the study indicated a significant impact on all the five human resource strategies on the level of employee loyalty and job performance. From the data results, it can be deduced that employee engagement presented the lowest impact on both employee loyalty and job performance while reward and performance appraisal systems had the highest impact. Relatively, based on the study results, there exists a direct correlation between employee loyalty and job performance. This finding implies that an increase in the level of employee loyalty directly results in an increase in job performance.
An effective reward and performance appraisal system positively influences employee motivation, thus encouraging them to remain loyal to their organization. A reward system can be divided into monetary and non-monetary type of system. Research carried out by Harunavamwe and Kanengoni showed that both monetary and non-monetary systems are essential in influencing employee loyalty (3929). Therefore, organizations need to ensure that they incorporate both aspects into their reward systems to optimize the level of employee loyalty and job performance.
Organizational commitment to the development and training of employees is also vital in increasing loyalty among employees. Training and development by an organization provide employees with a sense of belonging to the organization, thus making them feel obliged to commit themselves to the organizational objective. A favorable working environment that is respectful with a low level of stress illustrates a high impact on employee loyalty. Shagvaliyeva and Yazdanifard suggest flexible working hours as a solution to creating a stress-free work environment with the benefit of higher job performance, both at the individual and organizational level (20). Open communication refers to both horizontal and lateral communication. For instance, effective communication between employees allows employees to attend to their duties effectively. It also helps in building a sense of teamwork. Additionally, employees also need to feel free to communicate with their bosses concerning personal or company issues. Such open communication aids in fostering their commitment to their organizational responsibilities.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Employee loyalty is vital to the success of any organization. It has become a source of competitive advantage in today’s human resource market. Most organizations are seeking to attract and retain their best employees to boost their performance. Organizations need to formulate effective human resource strategies and/or policies that offer them a competitive advantage through fostering a high level of employee loyalty.
As illustrated in the paper, research data highlights organizational commitment to the development and training of employees, employee engagement, effective reward and performance appraisal systems, and open communication as key strategies that have significant positive impacts on employee loyalty. In addition, an increase in employee loyalty illustrated a direct correlation with employee performance.
Hence, an organization that has a high level of loyalty among its employees will reflect a high level of performance, both at individual and organizational level. On the other hand, lack of effective strategies that increase employee loyalty in an organization will consequently result in a low level of performance. Therefore, based on the findings, I would recommend the integration of the five human resource strategies by organizations that are struggling to attract and retain competent employees to increase the loyalty of their employees and/or improve the performance of new and the existing employees.
Works Cited
Alrawabdeh, Wasfi. “How Employees’ Loyalty Programs Impact Organizational Performance within Jordanian Banks?” International Business Research 7.9(2014): 119-130. Print.
Harunavamwe, Martha, and Herbert Kanengoni. “The impact of monetary and non-monetary rewards on motivation among lower level employees in selected retail shops.” African Journal of Business Management 7.38 (2013): 3929-3942. Print.
Martensen, Anne, and Lars Grønholdt. “Internal marketing: a study of employee loyalty, its determinants and consequences.” Innovative Marketing 2.4 (2006): 92-116. Print.
Murope, George, and Yustin Bangi. “Examining the Influence of Management Practice and Attitudes on Employee Turnover: A Case of Kibaha District Council”. The International Journal of Business and Management 2.9 (2014): 11-18. Print.
Ong, Derek. “Expressions of Fresh Graduates: Employee Loyalty in Malaysia.” World 5.2 (2014): 92-106. Print.
Shagvaliyeva, Sussanna, and Rashad Yazdanifard. “Impact of flexible working hours on work-life balance.” American Journal of Industrial and Business Management 4.1 (2014): 20-23. Print.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary, 2016. Web.
Wan, Hooi. “Employee Loyalty at the Workplace: The Impact of Japanese Style of Human Resource Management.” International Journal of Applied HRM 3.1 (2012): 1-17. Print.