Introduction
Coca-Cola is one of the most popular soft drinks in the world. Now available in over 200 countries, estimates indicate that product sales stand at two billion each day (Conway, 2021b). These figures indicate that the soft drink has been highly successful. For success, a company must develop an efficient marketing strategy. Marketing strategies help establish short-term and long-term goals. An efficient marketing strategy will lead to increased sales and an increased market share. Coca-Cola’s brand value is estimated to be over $71 billion (Conway, 2021b). This paper will delve into the marketing strategy employed by the Coca-Cola Company that has resulted in the soft drink’s success.
The Marketing Mix
Place
Coca-Cola’s market is not restricted to a particular geographic location. The products are accessible all over the world, bar North Korea and Cuba. The production strategy for the company that involves franchising has been instrumental in promoting the drink in different locations. In addition to bottling their drinks, the local franchises create advertisements in their locations, helping the individuals relate to said advertisements. The Coca-Cola Company insists that the company mainly operates through these localized institutions, underpinning the importance of the institutions to the growth of the Coca-Cola brand.
Due to the localization of Coca-Cola brands, marketing campaigns involve geographic elements that specifically target consumers in a particular location. The company incorporates different national languages in its advertisements depending on the location. Brand packaging of the product also has an enormous influence on how the target market perceives the product. The product becomes personalized by packaging the soft drink in adapted packaging (Khan & Lee, 2020). By using these strategies, Coca-Cola has successfully localized its products despite being a global brand. However, the company itself controls the aspects of production to ensure quality is maintained. The campaigns in different locations also have similar themes, refreshment, happiness, and togetherness. Additionally, the company monitors the actions of the franchises to maintain a positive Coca-Cola brand.
Pricing
Coca-Cola adjusts the price of a Coca-Cola drink to reflect the economic status of the individuals. The affordability of the soft drink has prompted increased sales of the drink. By adjusting the prices, the company can market the drink to many customers and establish a wide customer base. However, the customer practices price discrimination depending on the location (Wang, 2021). Competitive pricing helps the company fight off its main competitor, Pepsi. Since the soft drink market is near saturation, the soft drink must establish appropriate pricing policies.
Products
The original Coca-Cola is the most popular product sold by the Coca-Cola Company. However, variants to the drink have crept up to adapt to diverse needs. Diet Coke, Coca-Cola Zero, and Coca-Cola Life have been introduced to attract customers who prefer fewer calories. Additionally, the parent company has several products available to consumers as substitutes for Coke including Fanta, Minute Maid, and Sprite. These products have their marketing campaigns different from Coca-Cola, but they help the parent company create diversity.
Promotion
Despite its dominant status in the soft drink market, Coca-Cola relentlessly promotes its products. Historically, Coca-Cola has always fully immersed itself in marketing. Twenty-five years since its inception, Coca-Cola’s marketing budget grew to over a million dollars. The Coca-Cola Company has launched several campaigns for its frontline soft drink Coca-Cola. These campaigns have been hugely successful, but they are capital intensive. Promotional activities for Coca-Cola products demand an excess of $4 billion annually (Conway, 2021a). Coca-Cola has also adopted social media marketing by using the available social media platforms, such as YouTube and Facebook for promotional videos.
The company also incorporates corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities to connect with the market and to promote the brand. CSR activities benefit a company by increasing the loyalty of customers, which translates to more sales and increased revenue (Rim & Song, 2017). Promotion campaigns also take the form of branded products. The company gives away branded merchandise such as clocks, caps, t-shirts, and napkins to grow the brand. Sponsorship of events, such as the Olympics, also endears the Coca-Cola brand to the consumers. Sponsorships help promote the social image and reputation of the company while also increasing popularity.
Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy focuses on the brand rather than the product. The soft drink company has continually created campaigns that portray Coca-Cola as more than just a soft drink but rather as a source of happiness. The association between Coca-Cola and the festive seasons has been crafted over the years and is continually enforced every holiday season. Coca-Cola’s Northern Lights advertisement was the first instance where the company associated the festive season with the soft drink (Luque Galan, 2021). Subsequent advertisements have followed this blueprint, the premise of the advertisements being joy and happiness.
Coca-Cola has continually used Santa Claus during the holiday season, and the association has promoted the association between the soft drink and happiness. Additionally, such a campaign as Taste the Feeling portrays different groups of people enjoying themselves, laughing, and dancing, with the common denominator between them being the soft drink (Luque Galan, 2021). Taste the Feeling follows the precedents set by the 2007 Coke Side of Life campaign and the 2009 campaign Open Happiness campaign. Innovative promotion strategies, such as the 2018 campaign, A Coke for Everyone, have been successful. The campaign involved branding Coke cans with consumers’ names, creating a personal connection between the user and the product. A Coke for Everyone was the first campaign specifically designed for social media. Consumers shared pictures of their names on drinks, encouraging others to purchase a drink with their names on it.
Market Segmentation
Most people can consume Coca-Cola, and the company targets every individual as a potential customer. However, Coca-Cola target young people in its advertisements (Wang, 2021). Coca-Cola heavily incorporates celebrities in their advertisements, and they have featured different celebrities, including Wayne Rooney, Aretha Franklin, Ray Charles, Keanu Reeves, and The Supremes (Wang, 2021). The celebrities appease the younger generation, who are more easily influenced by popular individuals. The advertisements used are also constantly improved and adjusted to current trends.
Coca-Cola does not particularly target a particular gender or individuals with a certain level of income. However, in terms of psychographic segmentation, the company also targets individuals who may shun Coca-Cola due to health risks. Coca-Cola Diet is a soft drink proposed as an alternative to the traditional Coca-Cola for individuals who may otherwise shun the drink (Slavin, 2017). The company also cashes in on nostalgic customers. As a product that many generations have consumed, Coca-Cola recognizes its place in family events. Marketing campaigns tailored around shared family time prompt nostalgia among the older generation as they reminisce on time spent with their families.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Coca-Cola’s greatest strength is the unique taste that the company has created using its secret recipe. The secret recipe has attained an almost mystical status and is one of the most protected secrets in the business world. Attempts to replicate the recipe have produced abysmal results. The preservation of the iconic taste promotes the drink since a buyer knows exactly what to expect. Little variance ensures predictability and enforces loyalty from its customers.
Weaknesses
The greatest setback facing Coca-Cola is the nutritional harm that the drink causes its consumers. Despite the popularity of the drink, the side effects of its consumption are public knowledge. Slavin (2017) contends that consumption of soft drinks poses a problem since it may result in obesity and increased mortality rates. To counter this weakness, the company has introduced healthier drinks, Coke Zero and Diet Coke. The drinks have lesser artificial sweeteners than the traditional Coca-Cola. However, the soft drink represents a case of a brand that is too big to fail. Despite the concrete evidence that consumption of the drink affects one’s health, the market share of the drink has only grown (Beebee, 2019). People continuously shun the side effects of the drink.
Opportunities
Coca-Cola creates campaigns with other companies especially to target fast-food consumers. Collaboration with other companies helps expand the drink’s market and entice new customers. Additionally, since the soft drink market is essentially an oligopoly, there is a limited chance of being upset by new entrants, and the company can enjoy its market share. The company also enjoys an ingrained predisposition to like Coca-Cola products due to its prevalence in media over the years.
Threats
The biggest threat to Coca-Cola is competition by Pepsi. Although Coca-Cola overshadows Pepsi, the latter has intensified its marketing campaigns. Coca-Cola responds to this threat by continually innovating new marketing strategies and investing heavily in marketing. Additionally, due to the sale of the drink in diverse locations, unique challenges arise from the political conditions, economic situations, and cultural differences. However, the company develops pricing mechanisms that align with the per capita income of the demographics of different countries (Wang, 2021). In developing countries, the drink tries to boost the sales volume instead of profits. Conversely, in developed countries, the company focuses more on making profits.
Since soft drinks are under increased scrutiny over the content within the drinks, some regions have legislation in place to limit the consumption of the drink. Additionally, due to the environmental effect of plastic bottles, there is mounting pressure on legislators to enforce packaging regulations for soft drinks. To address this threat, Coca-Cola pledges to make its packaging from recycled material by the year 2030 (Watkins & Schweizer, 2018). Additionally, due to the danger of obesity posed by Coca-Cola, the regulation of Coca-Cola consumption for young people, especially in the school environment, is essential.
Expressions of Interest
The expression of interest (EOI) is a key performance indicator (KPI) developed by Coca-Cola to track the effectiveness of its social media presence. The EOI is based on the social reads, the social shares, and total visits (Alameda & Martin, 2019). The formula for calculating the EOI is:
(Social read x 10) + (social shares x 5) + (SEO X 1) + total visits rank / 10. A higher EOI is preferable as it justifies the expenditure on their online campaigns.
Conclusion
Coca-Cola is one of the most renowned brands all over the world. The brand has implemented successful marketing strategies that attend to different demographics and ensure the growth of the brand. The drink has become part and parcel of popular culture, and it has squeezed itself into events, gatherings, and celebrations. The soft drink has exhibited incredible continuity by remaining in business for more than a hundred years. The adaptability of the marketing strategy to different demographics over time has ensured the continued growth of the drink. The growth of the drink can be attributed to effective marketing strategies.
References
Alameda, D., & Martín, I. (2019). Brand engagement and positive advertising. In J. A. Muñiz-Velázquez & C. M. Pulido (Eds). The Routledge Handbook of Positive Communication (3rd ed., pp. 167-177). Routledge.
Beebe, J. (2019). Should there be a soda tax? Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy Report.
Conway, J. (2021a). Coca-Cola Co.: ad spend 2014–2020. Statista.
Conway, J. (2021b). Coca-Cola Company – Statistics & facts. Statista.
Khan, H., & Lee, R. (2020). Does packaging influence taste and quality perceptions across varying consumer demographics? Food Quality and Preference, 84, 103-132.
Luque Galán, T. (2021). 100 years of Christmas: The story of how Coca-Cola has shared the gift of Christmas from 1920 to 2020 [Bachelor’s thesis, Universidad Loyola]. Institutional Repository of Universidad Loyola.
Rim, H., & Song, D. (2017). Corporate message strategies for global CSR campaigns. Corporate Communications: An International Journal, 22(3), 383–400.
Slavin, J. (2017). Do sugar-sweetened beverages cause obesity and diabetes? Annals of Internal Medicine, 167(1), 71-72.
The Economist. (2020. The cola wars made Pepsi and Coke “the world’s best marketers.
Wang, J. (2021). How Coca-Cola and Pepsi use segmentation in consumer product industry. In 2021 International Conference on Public Relations and Social Sciences (ICPRSS 2021) (pp. 866-870). Atlantis Press.
Watkins, E., & Schweitzer, J. P. (2018). Moving towards a circular economy for plastics in the EU by 2030. Institute for European Environmental Policy.
Appendices
Appendix 1: Expenditure
Coca-Cola spend on advertising over the years. Data from Statistics (Conway, 2021a).
Appendix 2: Market Share
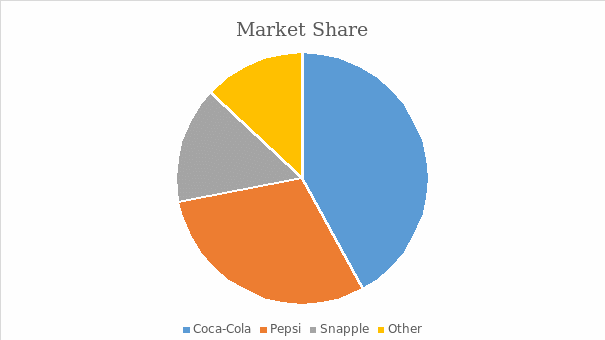
Soft Drinks’ Market Share In the United States. Data available on The Economist (The Economist, 2020).