Walmart is a giant global retail business among the various firms existing in the market today. According to Carbonara (2018), while retail companies keep changing, others remain the same, with Walmart appearing first in the Forbes Global 2000 list, despite the slip in rank in 2016 (Carbonara, 2018). Strategically, the entity continued with the e-commerce acquisition plan, until, later, it announced to buy India’s largest company- Flipkart (Carbonara, 2018). This assignment aims to analyze Walmart’s case study and examine its performance in destination countries such as India and the Czech Republic.
Political, Economic, and Cultural Elements
India is a democratic state, and it runs a federal form of government. Businesses within the Indian economy are subjected to rules and policies instituted by the state’s authority. The political environment is shaped by factors such as politician’s interests and ideologies of different parties. The tax system is developed, including income, service, and sales tax imposed by the Union government. Local bodies take care of taxes such as utilities, while privatization is a significant influence in the economy.
Since the introduction of reform policies in India, the country’s economy remains stable. The emerging economy facilitates the operation of organizations, as there are market opportunities. The Indian government demanded foreign businesses to invest about $100 million in India (Walmart Case study, n.d.). Another notable economic factor is inflation, whereby India has a high inflation rate that could impact income redistribution, especially to foreign firms such as Walmart.
To succeed in the Indian market, a business must take into consideration the cultural environment factors. The country has a traditional outlook that can challenge any firm wishing to conduct trade within the economy. Unlike in the US, where Walmart’s store sizes are convenient to clients, the preferences of the Indians are different. Other cultural factors in India that could impact businesses include lifestyles shaped by religion, for instance, certain eatery habits. Therefore, such social issues can affect how Walmart will approach the new market.
Obstacles facing Walmart and other foreign retailers in India
include infrastructural differences, political, cultural, and regulatory barriers. Indian market is an emerging one, but the country’s culture is strong and different from that experienced by Walmart in the Western countries. Customers’ buying habits and preferences are unique, with people opting to shop from small business units. India has poor infrastructure, such that the government demands foreign investors to pay a significant amount of money that goes to back-end operations, transportation services, and cold storage facilities. Furthermore, the Indian government imposes some restrictions through taxation, which can be an obstacle to businesses. Cultural issues are common as not all Indians support American products, and the firm’s Chief Executive officer (CEO) has a difficult task to counter hindrances, including language problems.
Quadrant of the Matrix
By analyzing the global market situation in India and prospects of Walmart, a matrix quadrant that would be applicable is B – joint venture and licensing. The following figure shows a matrix quadrant for the global retailing market entry approach framework for Walmart.
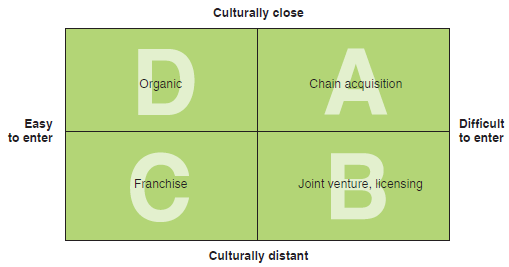
The rationale behind this section is that when comparing Indian and Western cultures’ characteristics, they are distant. Such a gap makes it difficult for Walmart to penetrate into the new market. In that case, the best alternative would be to pursue a joint venture with local companies such as Flipkart through legal licensing to operate in a foreign market (Bhaskaran & Bandookwala, 2020). Typically, investments in foreign markets are a mutual benefit for both businesses and the local economy. According to Nougarahiya et al. (2021), India has the potential to thrive economically through relief measures from the government and global retailers’ support. Walmart needs to partner with Indian farmers to improve services and products, and this collaboration will help understand the nature of the new market.
Elements in the Czech Republic Environments
Similar to other government systems in the world, the Czech Republic enacts policies to guard local economies and people. In case the authority perceives business as a threat to citizens, regulatory measures are introduced to enable growth opportunities when necessary. The government is entitled to continuity work to improve prosperity. The Czech Republic leaders will promote ideology in combining with other crucial goals, implying the government will encourage continuity development if business motives are productive.
Economically, vital inputs to enterprises are the nature of fiscal or tax policies. Strictly, these aspects of the political environment bear tremendous economic impacts on firms. For an organization such as Walmart to succeed in the Czech’s economies, it must adequately investigate the features and analyze implications for both the short and long-term. The Czech government established a tax system for revenue collection in 1993 (Lipkova et al., 2017). Tax regulations are paramount, and recently, the policy was subjected to extensive amendments due to commercial law provision changes.
The country has advanced infrastructures that make it considered the best country in Central and Eastern Europe. Direct highways connect to Germany, Slovakia, and Poland. Railway network links to the Europe region, and direct flights that serve geographies such as Asia and North America facilitate business operations. Moreover, Czech has stable politics, an educated workforce, and an economic environment described as an EU single market, which determines the quality of business performance (Kozubikova et al., 2019). The Czech Republic is essentially a country made up of small towns and cities. Agriculture is a significant activity due to its vast land extent.
Market Expansion Strategy in Czech
Based on environmental reviews, as one of the European countries, Czech has considerable stable economies in terms of declined inflation due to the factors such as capital flows. Improved transport and communication systems support trade in the countries. Moreover, trade relations and openness dampen commodities’ prices due to the substitution of domestically produced goods with cheaper foreign options. With that entry of foreign business such as Walmart would contribute to low consumer prices in the short and long-term. Reflecting on quadrant matric, an organic system applies to Czech due to Czechs’ cultural closeness with Western culture. Furthermore, political situation and trade policies enable a firm to enter quickly into the market, adopting a cost positioning strategy.
Utilities for Customers
Walmart strives to create and increase products’ value when entering new markets to enhance satisfaction, boost sales, and drive earnings. In form utility, Walmart must consider how to meet customer wants, needs and preferences. For example, Walmart could design items to target specific age groups per the needs and invest in gathering customers in the Czech market to understand people’s cultural preferences. Alternatively, the business may create a form utility of price discounts to integrate the cost position strategy effectively.
Walmart will need to maximize the availability of products in Czech markets so that clients can buy during a convenient time. The move will require logistical planning, market research, and adjusting the production process. Creating time utility will include knowing days and hours when Czech people prefer to shop, for instance, knowing when is the best time to open stores. Place utility will be meet by availing commodities to areas where shoppers will access them conveniently. Using market studies, Walmart must understand market dynamics such as size and geographic distributions to determine stores’ localities. Increasing convenience for buyers will be vital in attracting the market.
At the same time, ownership or information utility refers to the amount of usefulness and perceived value of commodities. Walmart will need to boot possession utility by marketing product use as benefits and financing benefits to make clients enjoy while paying less money. Giving discount privileges on top of low prices will be a strategic approach to improve ownership utility. As product quality becomes an essential aspect, Czech consumers can shift attention to well-recognized brands and forego cheap commodities. Thus, discount stores would succeed and dominate the market as possession utility become a competitive advantage for Walmart.
A SWOT Analysis for Walmart in the Czech Republic
Strengths:
- Strong market power over other supplies in the Czech
- Has international presence; therefore, easy to earn Czech market
- Cost leadership strategy to attract market
Weaknesses:
- Thin profits from a low-price approach (Walmart Case Study, 2021)
- Other firms in the Czech market can easily copy the business model
Opportunities:
- Walmart can conduct strategic alliance with other firms operating within the Czech market
- The company can improve on quality standards to attract more customers and retain the market (Wilbert, 2018)
- Walmart has an opportunity to expand more to market neighboring Czech such as Poland
Threats:
- Competition from rivals such as Amazon, Target, and eBay (Kestenbaum, 2017)
- Czech political and legal factors such as taxation might hurt Walmart’s profit margin even further.
References
Bhaskaran, P. B., & Bandookwala, N. (2020). Walmart’s acquisition of flipkart: Emerging paradigm of the digital era. South Asian Journal of Business and Management Cases, 9(1), 24-39. Web.
Carbonara, P. (2018). Walmart, Amazon top world’s largest retail companies. Forbes, Web.
Kestenbaum, R. (2017). Is Walmart good or bad for America? The question may be outdated. Forbes. Web.
Kozubikova, L., Kotaskova, A., Dvorsky, J., & Kljucnikov, A. (2019). The impact of political factors ‘perception on suitability of international business environment: The case of startups. Economics and Sociology, 12(1), 61-79. Web.
Lipkova, L., Gress, M., & Poncarova, A. (2017). Tax systems in the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic: comparison with an emphasis on income tax. Economic Annals-XXI, 165. Web.
Nougarahiya, S., Shetty, G., & Mandloi, D. (2021). A Review of e-commerce in India: The past, present, and the future. Research Review International Journal of Multidisciplinary, 6(03), 12-22. Web.
Walmart Case study. (2021). Case study introduction. Web.
Walmart Case study. (n.d.). Can Walmart crack the retail code in India? Web.
Wilbert, C. (2018). How Wal-Mart works. HowStuffWorks. Web.